1-31 #BacktoWork : Intel’s CEO Patrick Gelsinger has made 4 commitment; US may enforce more restrictions on Huawei; SK Hynix has reportedly reshuffled its CIS team; etc.
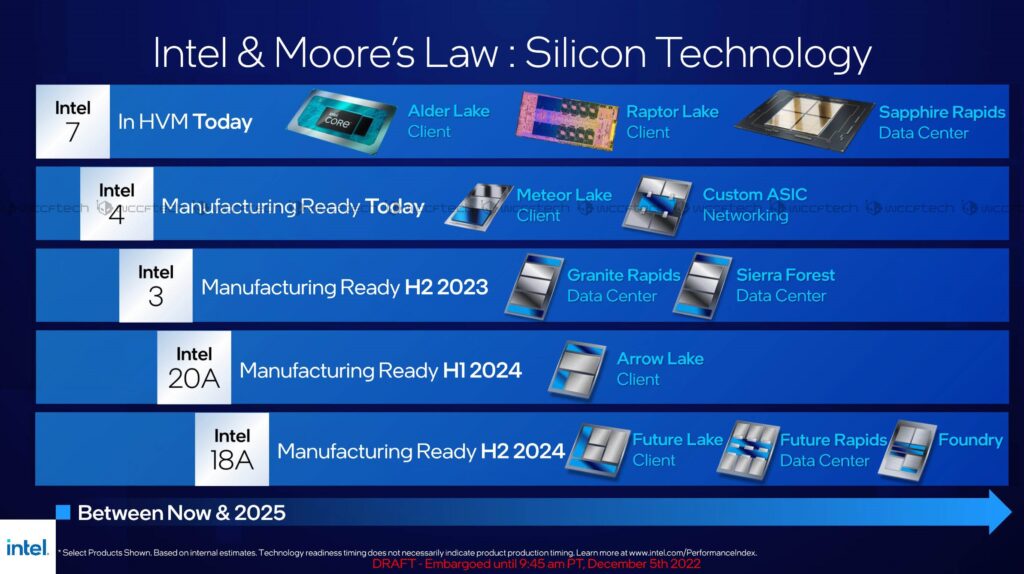
Intel’s CEO Patrick Gelsinger has made 4 commitments: One, deliver on 5 nodes in 4 years, achieving process performance parity in 2024 and unquestioned leadership by 2025 with Intel 18A. Two, execute on an aggressive Sapphire Rapids ramp, introduce Emerald Rapids in 2H23 and Granite Rapids and Sierra Forest in 2024. Three, ramp Meteor Lake in 2H23 and PRQ Lunar Lake in 2024, and four, expand our IFS customer base to include large design wins on Intel 16, Intel 3 and 18A in 2023.(CN Beta, WCCFTech, Seeking Alpha, Hardware Times, Twitter)

U.S. power chip maker Wolfspeed is planning to build a factory in Germany for more than EUR2B (USD2.17B). The German auto supplier ZF will hold a minority stake. Production should begin in 4 years at the site in the small southwest German state of Saarland. (Laoyaoba, Euro News, Reuters, Yahoo)

IBM is slashing 3900 jobs, about 1.5% of its global workforce. The cuts will cost the company around USD300M and will mainly impact its spinoff IT management outfit called Kyndryl as well as a part of its AI unit Watson Health. It came as IBM’s report for the fourth quarter revealed its cash flow was at USD9.3B – below its target of USD10B, with CEO Arvind Krishna blaming factors such as exiting Russia, wage inflation and a strong dollar for the drop.(Laoyaoba, Reuters, Computing, NZ Herald)
Leaders in the UK tech community have once again called out the government on its failure to implement a semiconductor strategy, writing to Prime Minister Rishi Sunak to publish the long-awaited roadmap as a “matter of urgency”. The open letter was signed by tech leaders from the likes of techUK, Tech London Advocates, Birmingham Tech and the Raspberry Pi Foundation. The letter also attracted signatures from microchip heavyweights such as Hermann Hauser, the founder of Acorn, from which semiconductor giant Arm was spun out, and Jalal Baghleri, former CEO of Dialog Semiconductor. (UKTN, Laoyaoba, Bloomberg, Tech London Advocates, The Register)

Several million microchips produced by Dutch manufacturers, including NXP and Nexperia, wound up in Russia in 2022 in shipments that were handled by resellers after sanctions were in place as a consequence of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Hundreds of deliveries were made to three Russian companies connected to that country’s defense industry. Both companies said they comply with all sanctions rules, that they do not do business with Russian firms, and that their clients are forbidden from selling the microchips to Russian organizations. (NOS, NL Times, CN Beta)
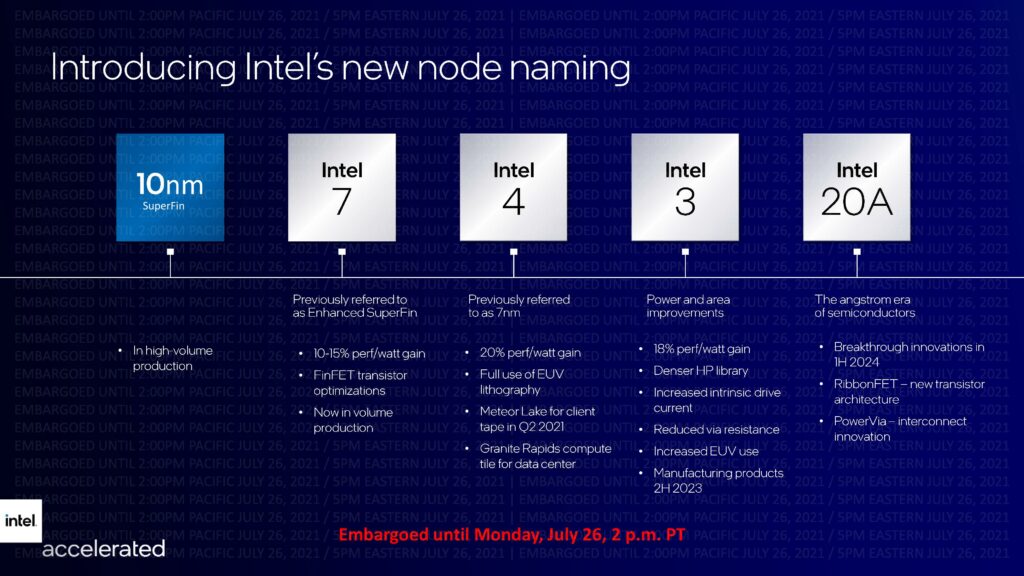
Intel Foundry Services (IFS) contract chipmaking division landed an order from a major “cloud, edge, and datacenter solutions provider” for producing chips on Intel 3 production node. The company has always tailored its Intel 20A and Intel 18A (2nm and 1.8nm-class, respectively) for its foundry customers. In contrast, its current and upcoming Intel 7 (10nm Enhanced SuperFin), Intel 4 (7nm with EUV), and Intel 3 (7nm+ with EUV) nodes were designed primarily with Intel in mind. So winning a major customer with Intel 3 — which is set to be production ready in 2024 — is clearly an achievement for the processor giant. (Laoyaoba, Tom’s Hardware)
Samsung has not developed any flagship Exynos chipset for its Galaxy S23 this year, instead choosing to exclusively use the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 for the remainder of 2023. However, this deal made with Qualcomm is only said to be temporary as behind the closely guarded chip development facilities, Samsung’s work on a next-generation Exynos SoC is slowly being carried on. will make a comeback of meaningful proportions as the development of the new Exynos for the Galaxy S25 is underway. Samsung is said to commence production of its second-generation 3nm GAA wafers in 2024. (My Drivers, WCCFtech, Joongan)
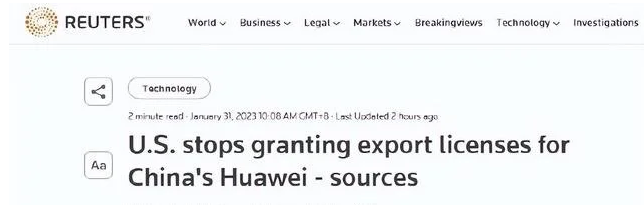
In 2019 the US placed Huawei on a trade blacklist, which meant that US companies required a special license to continue trading. Licenses were granted to the likes of AMD, Intel and Qualcomm, the latter was allowed to ship 4G-only chipsets. Licenses continued to be granted during the early days of President Biden’s administration, but now rumors say that the US is looking to expand the list of banned items. The new additions are said to include 4G tech, Wi-Fi 6 and 7, tech related to artificial intelligence as well as high-performance and cloud computing. New licenses for 4G items are already being denied. As for old licenses, the Commerce Department is allegedly looking to revoke all old licenses. (GSM Arena, Reuters, The Standard)
The US National Science Foundation (NSF) has awarded USD50M to an R&D partnership between Ericsson, IBM, Intel and Samsung to work on next-generation chips. The partnership is part of NSF’s Future of Semiconductors (FuSe) initiative. NSF will team with Ericsson, IBM, Intel, and Samsung to invest in multiple projects across a broad front but based on “co-design” approaches. (SamMobile, EE News, RS News, My Drivers)
BOE has showcased a 110” 8K naked-eye 3D screen with a high refresh rate of 120Hz, and allows users to watch high-definition 3D effects from any angle without wearing any auxiliary equipment. The 3D display terminal uses innovative lens array technology, with Mini LED and quantum dot backlight technology. At this stage, this product can achieve a screen distance of 1.5 meters, and with the continuous upgrading of the product, this distance will be greatly increased.(My Drivers, DoNews)

Apple will launch a foldable iPad with a carbon fiber kickstand sometime in 2024, according to TF Securities analyst Ming-Chi Kuo. He expects an “all-new design foldable iPad” to be the next big product launch in the iPad lineup, with no other major iPad releases in the next 9 to 12 months. He indicates that a carbon fiber material will be used for the iPad’s kickstand to make it light and durable. Chinese polishing and bonding supplier Anjie Technology will reportedly be the new beneficiary of the foldable iPad. Based on Apple’s iPad plans, Kuo said he was taking a “cautious approach” to iPad shipments for 2023, predicting a year-on-year decline of around 10-15%. However, he expects the 2024 foldable model to “boost shipments and improve the product mix”. (Twitter, CN Beta, My Drivers, MacRumors)
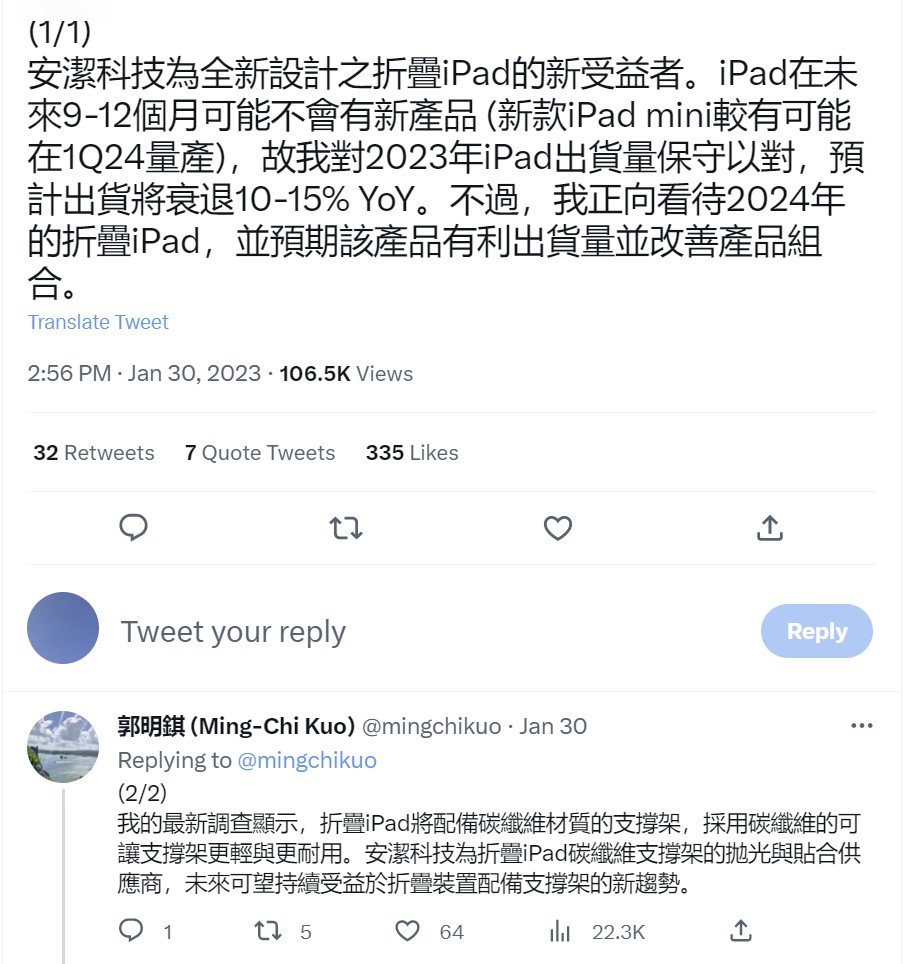
OnePlus will allegedly launch its foldable smartphones V Fold and V Flip, according to the trademarks filed by the company. They are being tested in many regions, including Europe. (GizChina, Android Headlines, Twitter)

SK Hynix has reportedly reshuffled its CMOS image sensor (CIS) team in a bid to shift focus from expanding market share to developing high-end products. SK Hynix is a smaller player in the field and in the past had focused on low-end CIS with 20MP or below resolution. The company has however started to supply its CIS to Samsung in 2021. It provided its 13MP CIS for Samsung’s foldable phones and in 2022 provided 50MP sensors for the Galaxy A series. Still, the overall demand for CIS has dropped in recent years as smartphones that mainly use them are suffering from a slowdown in demand. This has been especially poignant for mid-tier phones due to their unit prices dropping in response to low consumer demand. SK Hynix has been reducing its CIS output in light of this and is also reducing its inventory. (The Elec)
Sony Group has transferred production of cameras sold in the Japanese, U.S. and European markets to Thailand from China, part of growing efforts by manufacturers to protect supply chains by reducing their Chinese dependence. Sony’s plant in China will in principle produce cameras for the domestic market. Sony offers the Alpha line of high-end mirrorless cameras. The company sold roughly 2.11M units globally in 2022, according to Euromonitor. Of those, China accounted for 150,000 units, with the rest, or 90%, sold elsewhere, meaning the bulk of Sony’s Chinese production has been shifted to Thailand. Canon in 2022 closed part of its camera production in China, shifting it back to Japan. Daikin Industries plans to establish a supply chain to make air conditioners without having to rely on Chinese-made parts within fiscal 2023.(Laoyaoba, CN Beta, Asia Nikkei)

SK On is planning to expand its electric car battery production capacity in South Korea to meet rising demand from customer Hyundai Motor. Hyundai Motor has started construction of a new EV production facility at Ulsan. SK On is planning to start spending on its facilities at Seosan in 2023 with the aim to start commercial production in 2024 to supply Hyundai with batteries for EV made at Ulsan. SK On is expected to spend around KRW500B to expand Seosan’s current capacity of 5GWh a year to 10GWh. Genesis G80, GV60, and GV70 currently use batteries from SK On.(The Elec, Techgoing)
The battery-making joint venture between SK On and Ford is expected to use equipment supplied by a Chinese company for their factory in the US. It seemed unlikely that Zhejiang Hangke would win an order from BlueOval SK initially due to the ongoing trade war between the US and China. Hangke is expected to supply PPC and formation equipment to be used at BlueOval SK’s factories in Kentucky and Tennessee that are being currently built. The Chinese company won supply deals for back-end equipment from SK On in 2022. Zhejiang Hangke has recently signed USD146M battery equipment supply deal with the joint venture.(The Elec, Kaikin Media, Market Screener)
South Korean electric vehicle battery maker SK On will develop a new battery anode with US firm Urbix. The pair will collaborate on the development of the anode. If the development is successful, SK On will procure the anode from Urbix and use them at its battery factories in the US. The 2-year contract will be extended if both companies agree to continue their partnership. Urbix, founded in 2014, has technologies related to the processing of environmentally friendly, natural graphite. It is building a production facility in Arizona with an annual capacity of 1,000 tonnes per year and is aiming to expand this to 28,500 tonnes by 2025. (The Elec, Manufacturing Dive, Biz Journals)


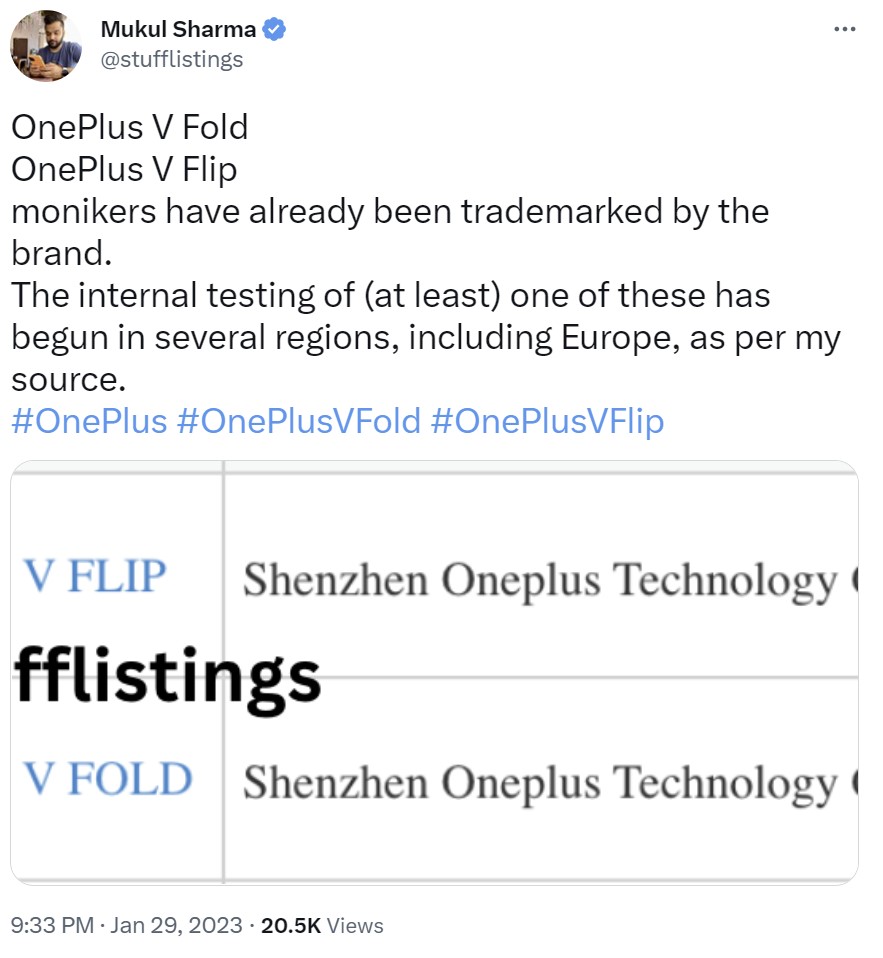
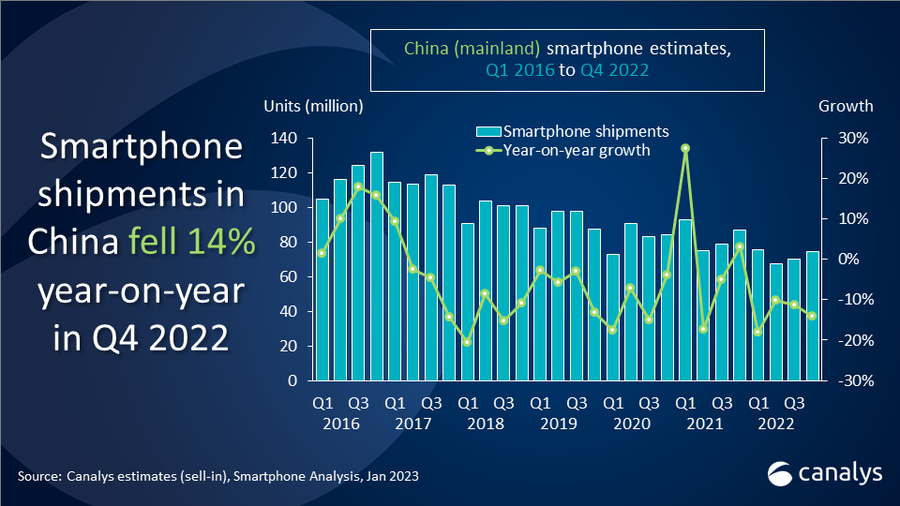
According to Canalys, Mainland China’s smartphone market finished 2022 with an annual shipment of 287M units, a YoY decrease of 14%. This is the first time since 2013 that China’s market shipment has fallen below 300M units. The 2022 crown was taken by vivo, while Honor and Apple ranked second and third respectively. Apple reached an all-time-high market share of 18% in China thanks to its aggressive promotions and demand in the high-end segment remained resilient. In 4Q22, despite the sales season, the Chinese market only managed to ship 74.4M units, recording a 14% YoY decline. (Laoyaoba, Canalys)
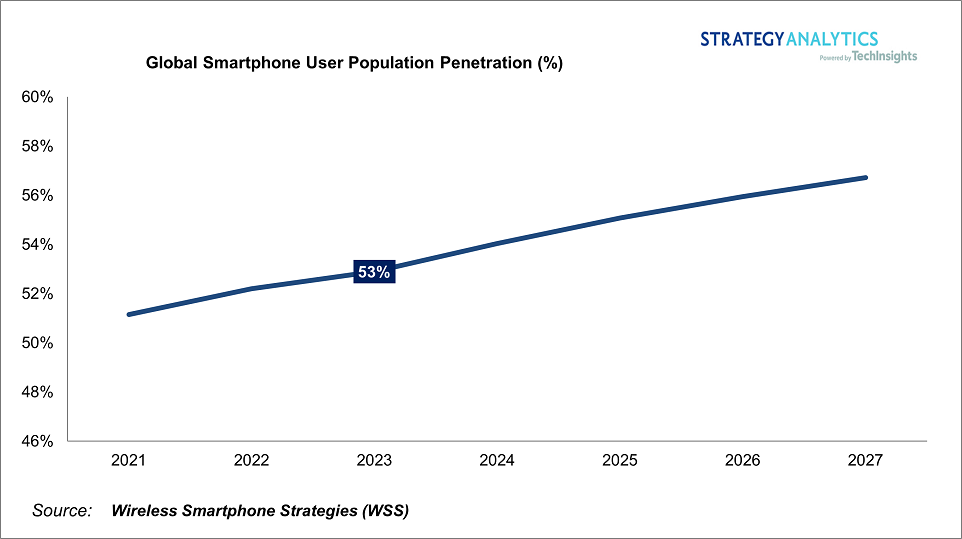
According to Strategy Analytics, the global smartphone user base will grow by 11% from 2023 to 2027. The global penetration rate of smartphones will continue to rise steadily. In the short term, it is due to the growth stimulated by the demand for home office during the epidemic, but the long-term growth momentum comes from emerging markets such as India, such as the upgrade demand for functional phones. (Laoyaoba)
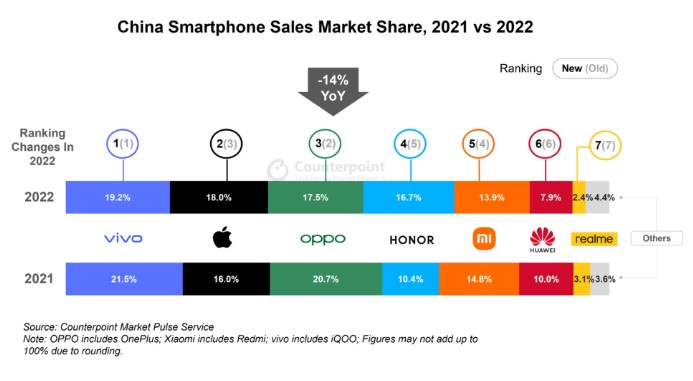
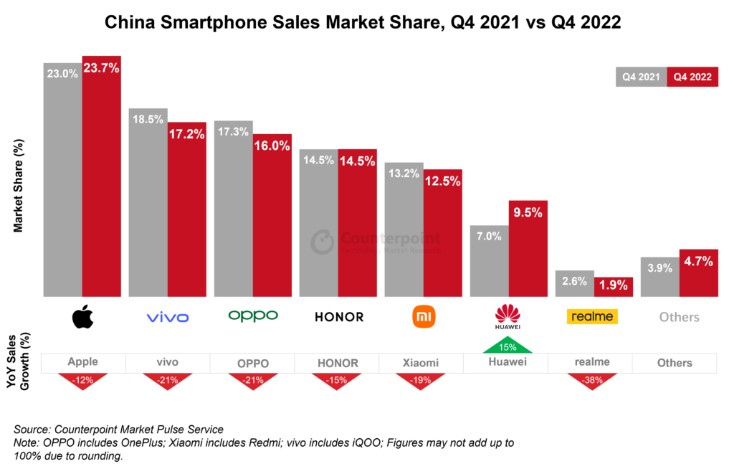
According to Counterpoint Research, China’s smartphone sales declined 14% YoY in 2022 to record their fifth consecutive year of decline. Apple’s sales outperformed the country’s market in 2022, falling by only 3% YoY. Major Android OEMs such as OPPO (-27% YoY), vivo (-23% YoY) and Xiaomi (-19% YoY) saw big YoY declines. China’s 4Q22 smartphone sales declined 15% YoY. All quarters in 2022 saw double-digit YoY sales declines. (Laoyaoba, Counterpoint Research)
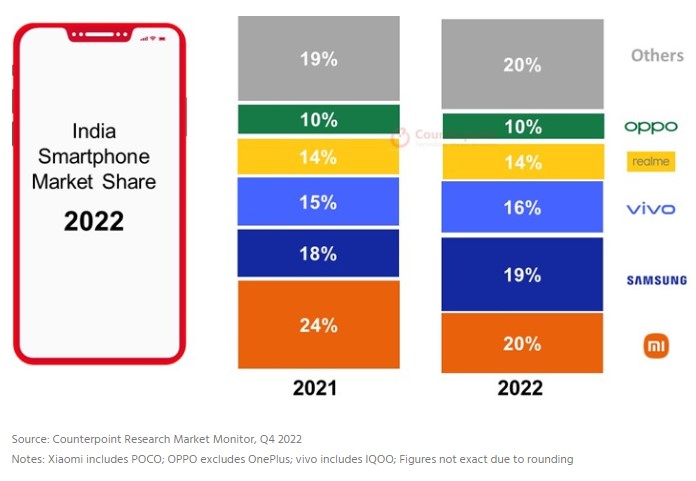
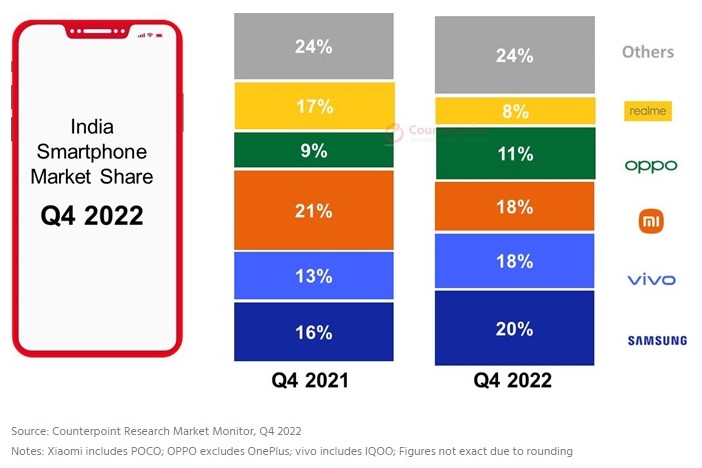
According to Counterpoint Research, premium segment (>INR30,000 or ~USD365) contributed 11% to India’s smartphone shipments and 35% to market revenue in 2022, the highest ever. Samsung led the market in 2022 in terms of shipment value share with a 22% share, followed by Apple. However, in terms of shipment volume, Xiaomi led the market in 2022 with a 20% share, closely followed by Samsung. But Xiaomi slipped to third position in 4Q22 with Samsung and vivo capturing first and second spots respectively. (Counterpoint Research)
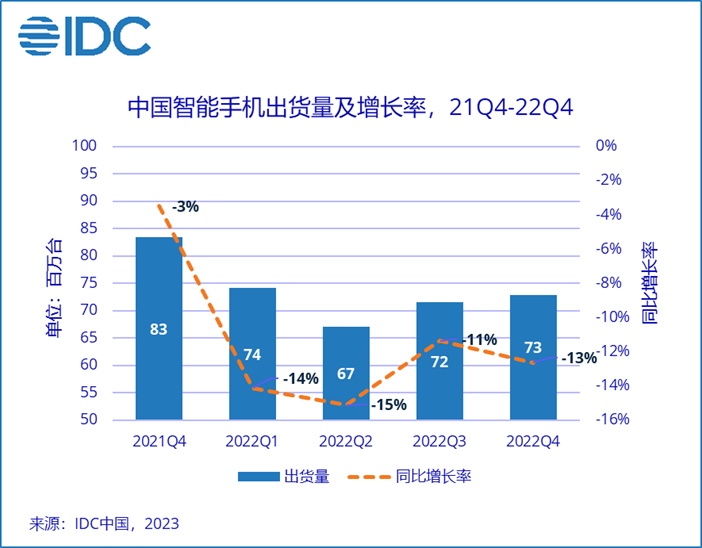
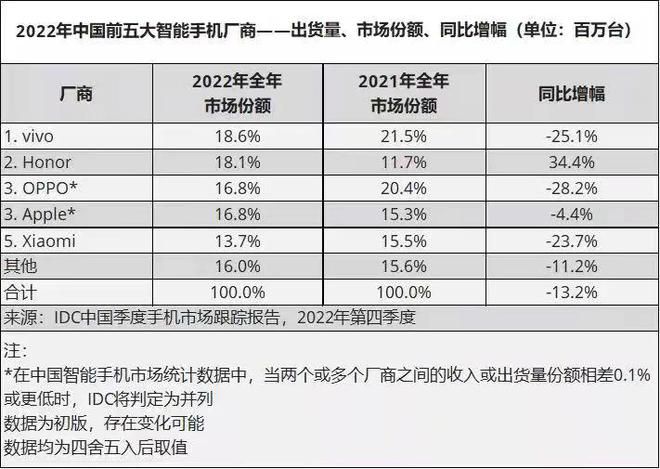
According to IDC, in 4Q22 China’s smartphone market shipped about 72.92M units, a YoY decrease of 12.6%. In 2022, China’s smartphone market will ship about 286M units, a YoY decrease of 13.2%, the largest decline in history. After a lapse of 10 years, China’s smartphone market shipments fell back to below 300M market. (CN Beta, IDC)
Manu Kumar Jain has left Xiaomi after 9 years playing an integral role in Xiaomi’s rise in India as a leader of the company’s operations in the Asian country. Jain revealed he would take some time off before taking on his new professional challenge, ideally in a new industry. Manu Kumar Jain vacated his position as Global VP at Xiaomi. (GSM Arena, Twitter)
In addition to 10,000 layoffs, Microsoft has hinted at some changes to its hardware lineup. Microsoft currently offers a range of hardware, including Xbox game consoles, PC accessories, Surface hardware, HoloLens headsets, and more. Microsoft has reportedly scrapped plans for a HoloLens 3 but recently hinted that it will make a “meaningful update” to the hardware when the time is right. Microsoft could also be looking at changes to its Surface lineup. Microsoft is also rumored to have scrapped plans for a dual-screen Surface Duo 3. (Pocket-Lint, The Verge, Microsoft)
Apple’s key supplier US manufacturing services provider Jabil has reportedly started manufacturing AirPods components in India and meanwhile, began shipping AirPods’ enclosures or plastic bodies to China and Vietnam. New Delhi has given initial clearances to more than a dozen of its Chinese suppliers to ramp up via joint ventures with Indian partners. AirPods assembler Luxshare Precision Industry, lens manufacturer Sunny Optical Technology Group, Han’s Laser Technology Industry Group and Shenzhen YUTO Packaging Technology are a few of them. (Apple Insider, Bloomberg, Yahoo, Benzinga)

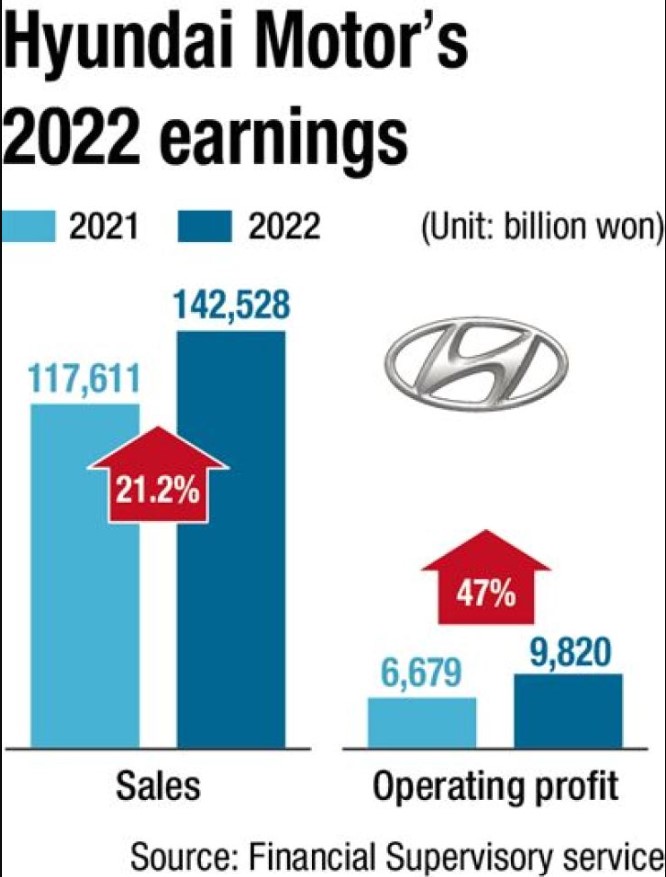
Hyundai Motor has unveiled its plan to focus more on selling electric vehicles (EVs) in the global market in 203, after posting record annual sales and operating profit in 2022. With the aims of selling 4.32M vehicles in 2023 in the global market and investing KRW10.5T in the car business, Hyundai Motor has also said it will increase global sales of its EVs, such as the IONIQ 6, IONIQ 5 N and the Kona EV. It has added that the market for eco-friendly vehicles will continue to grow in 2023, due to tightening environmental regulations in major countries and customers’ preference for cars that emit less pollution.(Korea Times)
Tesla CEO Elon Musk has indicated that the company’s Cybertruck will not be in full volume production until 2024. Cybertruck was originally announced in 2019, but has seen its production delayed several times. Pre-production was originally supposed to start in late 2021, but was delayed as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. It was then slated for sometime in 2023, a projection made a year ago.(The Verge, Electrek, Engadget)

He Xiaopeng, Chairman and CEO of electric vehicle firm XPeng, has revealed that the company aims to deliver 200,000 units of new electric vehicles (EV) in 2023. The navigation guided pilot (NGP) of XPeng will be delivered in 3Q23. He has said that autonomous driving should be regarded as the core of XPeng. Moreover, this is not the only goal of the company. XPeng will unveil five new models in 2023, including 2 brand-new vehicles and 3 updated versions of previous models. Both of the new cars are built on an 800V high-voltage platform.(Gizmo China, Pandaily, Auto)
