3-15 #Vaccinated : Samsung Foundry has shared the manufacturing details of the upcoming 3nm GAE MBCFET chip; SMIC is striving to regain orders particularly those for its 14nm FinFET process; Kyocera will shut down an LCD factory in China’s Jiangsu Province Nov 2021; etc.
Automotive semiconductors include MCUs, power semiconductors, sensors, and storage ASICs. Automotive semiconductors are widely used in various automotive subsystems, covering multiple sectors such as body, infotainment, chassis, powertrain, and driving assistance. Automotive semiconductors can be divided into five categories: 1) MCU, which is the micro-control unit of the car. Traditional cars use more than 70 MCU chips per car on average, and each smart car is expected to use more than 300 MCUs; 2) power semiconductors, mainly include Power Management ICs, LDO, DC/DC, MOSFET, IGBT, etc. Power semiconductors are the main components of automotive semiconductors; 3) Sensors, mainly including image sensors, MEMS sensors, and Hall sensors; 4) Memory, including various Embedded memory, SRAM, DRAM, FLASH; 5) ASSP, ASIC, analog, hybrid IC, FPGA, DSP and GPU except MCU. (CITIC Securities report)
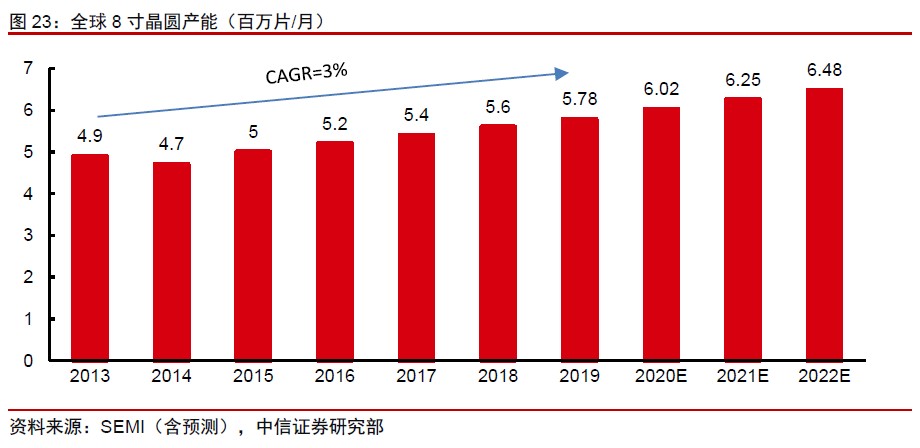
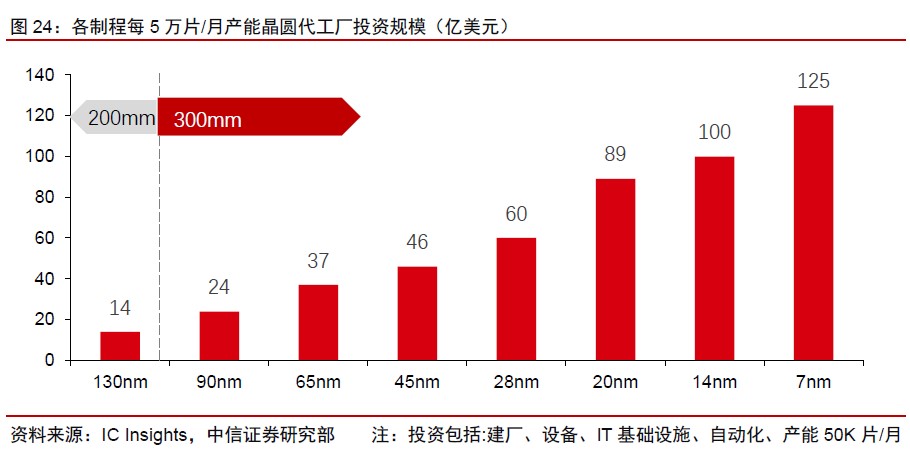
The input-output ratio of 8” is lower than 12”, and the difficulty in purchasing second-hand equipment is the main reason for the insufficient increase in new production capacity. From the perspective of investment efficiency, the current Capex capacity of 50,000 wafers/month to build a 90nm 12” wafer fab is about USD2.4B. The 0.13μm 8” wafer fab has an equivalent 12” production capacity per 50,000 wafers/month (112,500 wafers/month 8” production capacity) Capex scale is about USD3.15B. If the same is to purchase new equipment, the new 12” production line will be more efficient and the investment will be lower under the same capacity. In addition, the investment in the construction of a 12” wafer production line can also evolve to a higher process, and the technology is more scalable. (CITIC Securities report)
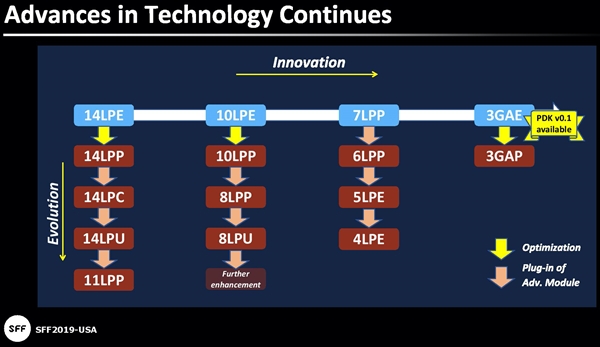
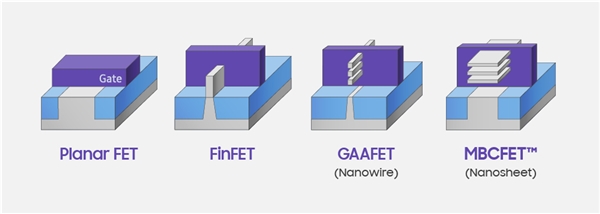
Samsung Foundry has shared the manufacturing details of the upcoming 3nm GAE MBCFET chip. Samsung has stated that the traditional GAAFET process uses three layers of nanowires to construct transistors, and the gate is relatively thin. Compared with 7LPP technology, 3GAE can achieve a 30% performance improvement. It also achieves a 50% reduction in power, and an 80% increase in transistor density. The company plans to mass-produce 3nm chips in 2022. (My Drivers, GizChina, CN Beta, IT Home)
With the US trade restrictions on Semiconductor Manufacturing International (SMIC) reportedly easing, the China-based pure-play foundry is striving to regain orders particularly those for its 14nm FinFET process, according to Digitimes. SMIC has managed to achieve a 95% yield with its 14nm semiconductor process. (Laoyaoba, WCCFtech, Digitimes, CN Beta)
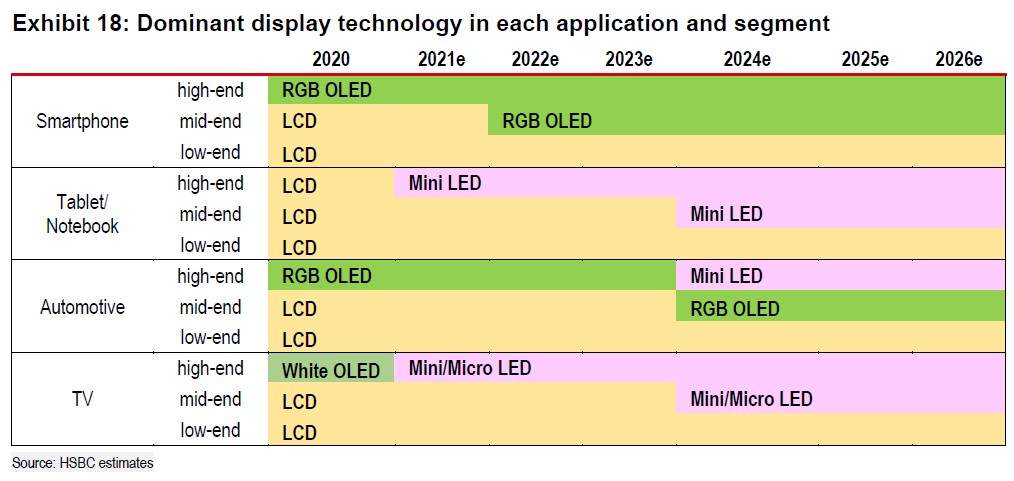
The roll out of mini and micro LED is going to be a long process. And while it has great potential for the whole supply chain, HSBC thinks progress may be uneven in terms of product quality, upgrades, and levels of profitability, especially during the development stage. However, to begin with, they think the yield rate and volume with be the most important factors in selecting the first round of winners. (HSBC report)
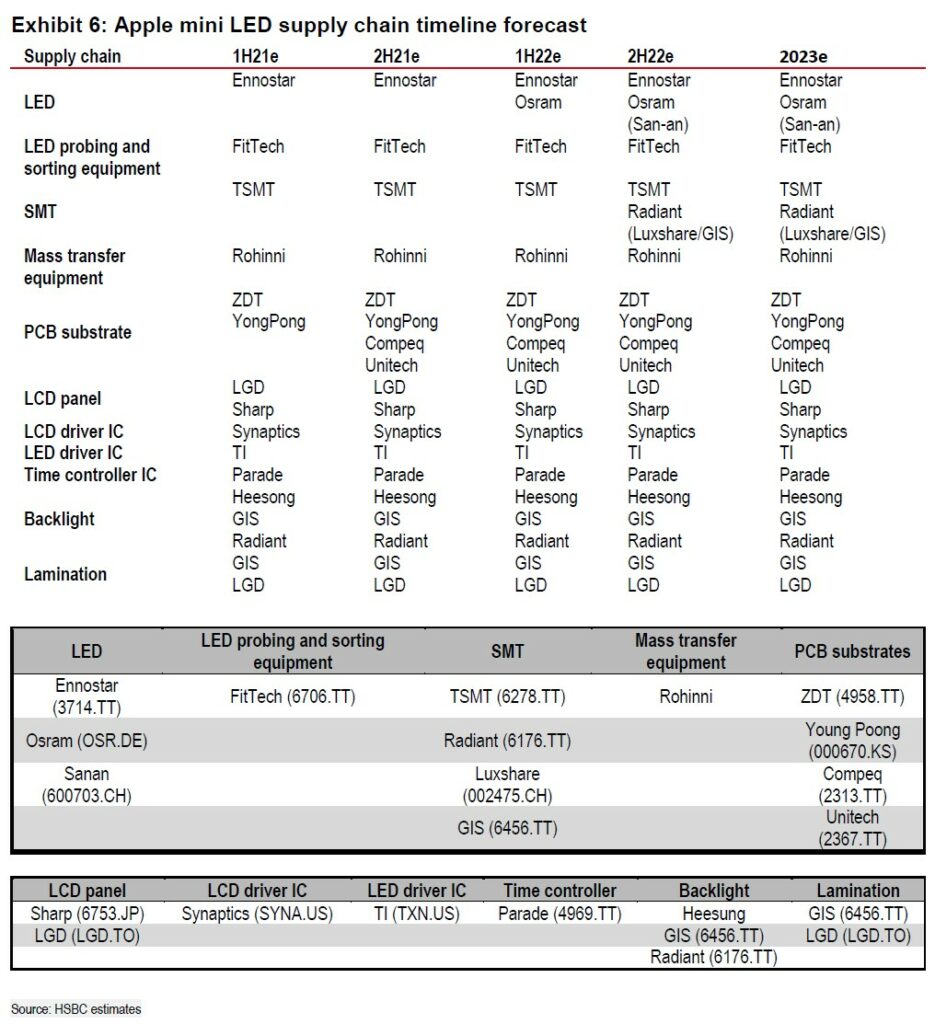
HSBC has illustrated their timeline forecasts for the Apple mini LED supply chain for 2021-2023. (HSBC report)
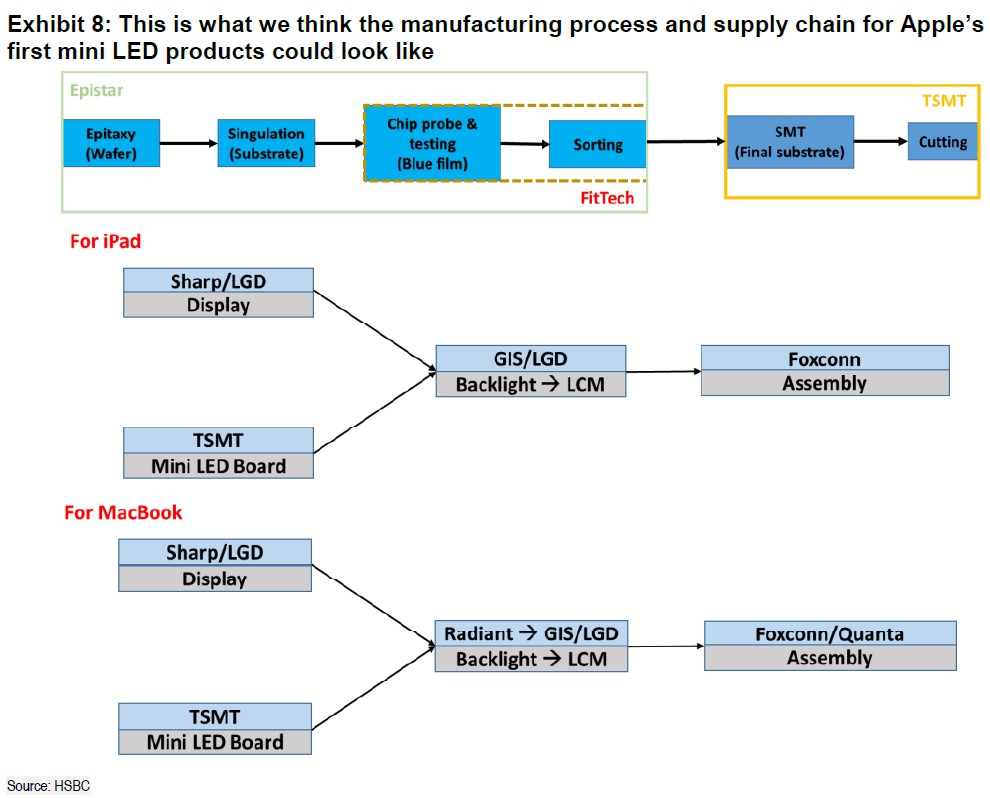
HSBC illustrates what they think the manufacturing process and supply chain for Apple’s first mini LED products could look like. They expect the manufacturing process to become the industry standard. (HSBC report)
As HSBC thinks RGB OLED may retain its dominant position in small application (mainly smartphones), they believe mini LED will gradually take over in the area of medium-sized applications such as tablets, notebooks, and automation. They also think the penetration rate of mini LED will rise in large applications, mainly TVs, once costs start to fall sharply in 2-3 years. (HSBC report)
Kyocera will shut down an LCD factory in China’s Jiangsu Province Nov 2021 on weak prospects for growth in the market for an older type of display used in automobiles. The plant in Zhangjiagang was opened in 1997 by Optrex, a Japanese liquid crystal display maker that Kyocera acquired in 2012. (CN Beta, Nikkei)
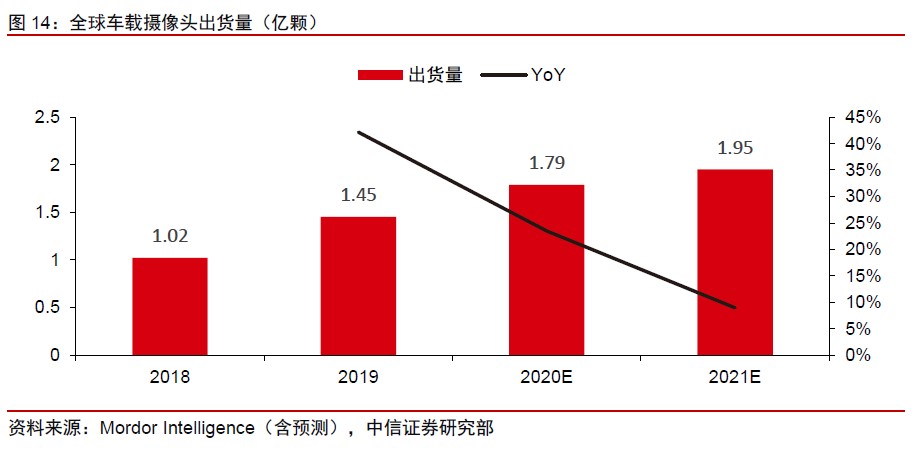
According to Mordor Intelligence, shipments of in-vehicle cameras reached 145M units in 2019, and it is expected to be close to 200M in 2021. CITIC Securities predicts that the automotive CIS market will be close to USD1B in 2019. In the future, as the penetration rate of assisted driving and ADAS continues to increase, the average CIS units per car will further increase, driving a compound growth rate of over 30% in the market size. In the long run, based on the calculation of 10 units, they expect the long-term automotive CIS market to reach about USD10B, which is close to the phone CIS market (about USD15-20B market). (CITIC Securities report)
According to Morgan Stanley, memory shortages are quickly worsening for 2Q21 and customers are taking measures to ensure that they will not be caught in short supply. Since buyers are all doing this at about the same time, what was a mild shortage in 1Q21 has become more serious entering 2Q21, especially DRAM. Sell-through will be important but demand continues to improve in most memory-consuming segments, and expect DRAM prices to easily move up >50% from current levels, as in past cycles. This is currently not priced in the market. (Morgan Stanley report)
Global supply of DDR3 chips has fallen short of demand by at least over 30,000 wafers, which has been pushing up pricing for the memory. Samsung has slowed down its plans to reduce low-density DRAM production capacity. In this wave of rising prices, the price of Samsung’s 2Gb DDR3 rose from USD0.95 to about USD3, a record high. Samsung’s 4Gb DDR3 is also in short supply, and the demand continues to be strong. After the Spring Festival, the price has risen to more than USD3.3, and many factories accept high-priced replenishment. (Digitimes, Sohu, Laoyaoba)
For Apple’s coming iPhone 13 cycle in 2H21, Barclays analyst Andrew Gardiner foresees a more tightly integrated version of the existing structured light system, which will enable the reduction in the notch. On the rear, they do not anticipate Apple to broaden the adoption of the Lidar 3D sensor beyond the Pro models. He also views the adoption of fingerprint-under-glass, that likely is added in the 2H21 iPhones, as a structural headwind for additional 3D sensing content at Apple and could be the security feature of the future. (Laoyaoba, MacRumors)
Panasonic’s outgoing Chief Executive Kazuhiro Tsuga has revealed that the company will need to reduce its heavy reliance on Tesla by making batteries more compatible with electric vehicles from other global carmakers. (CN Beta, Money Control, Reuters)
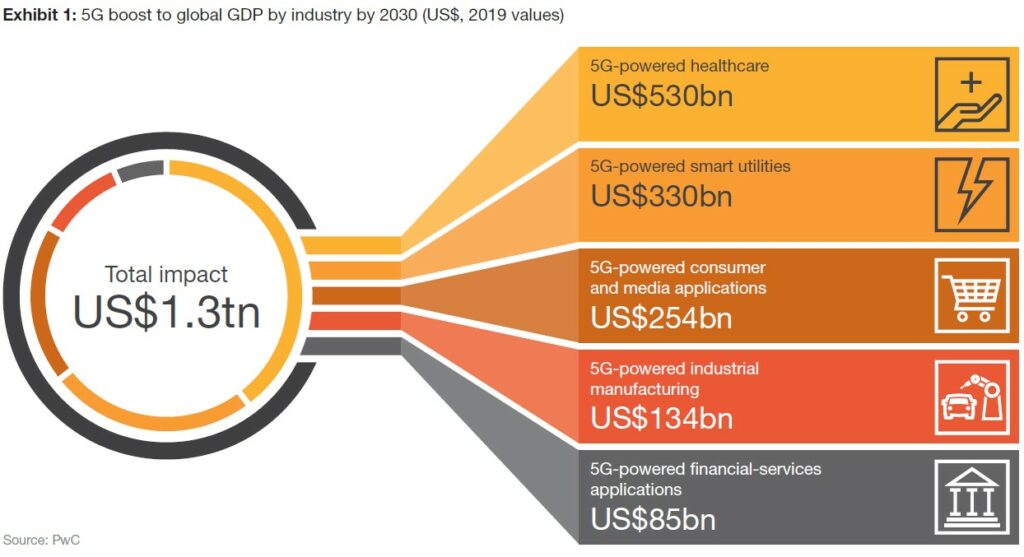
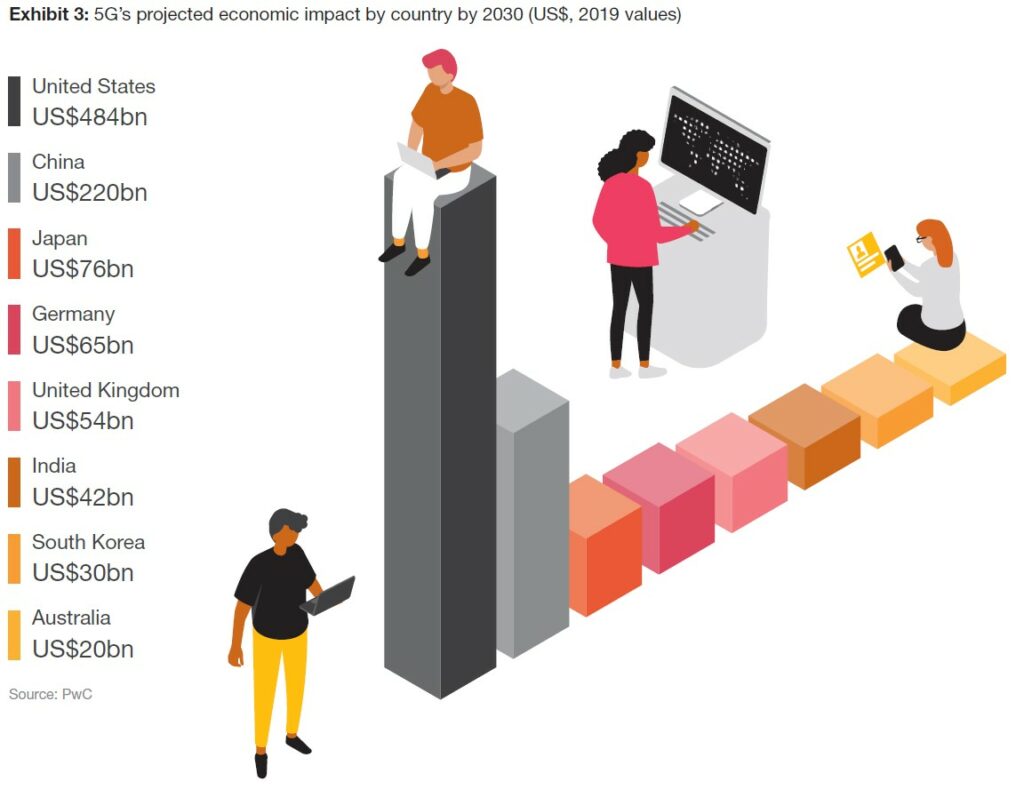
Healthcare will be far and away the biggest contributor to the economic gains from 5G: PWC’s model predicts that it could add more than half a trillion dollars to global GDP. But other industries also show significant potential, as 5G enables a vast wave of innovative solutions and use cases. PWC has analyzed use cases, both new and established, in 5 sectors—healthcare, smart utilities, consumer and media, industrial manufacturing, and financial services—and found that, in aggregate, the adoption of 5G will add USD1.3T to global GDP by 2030. (PWC report)
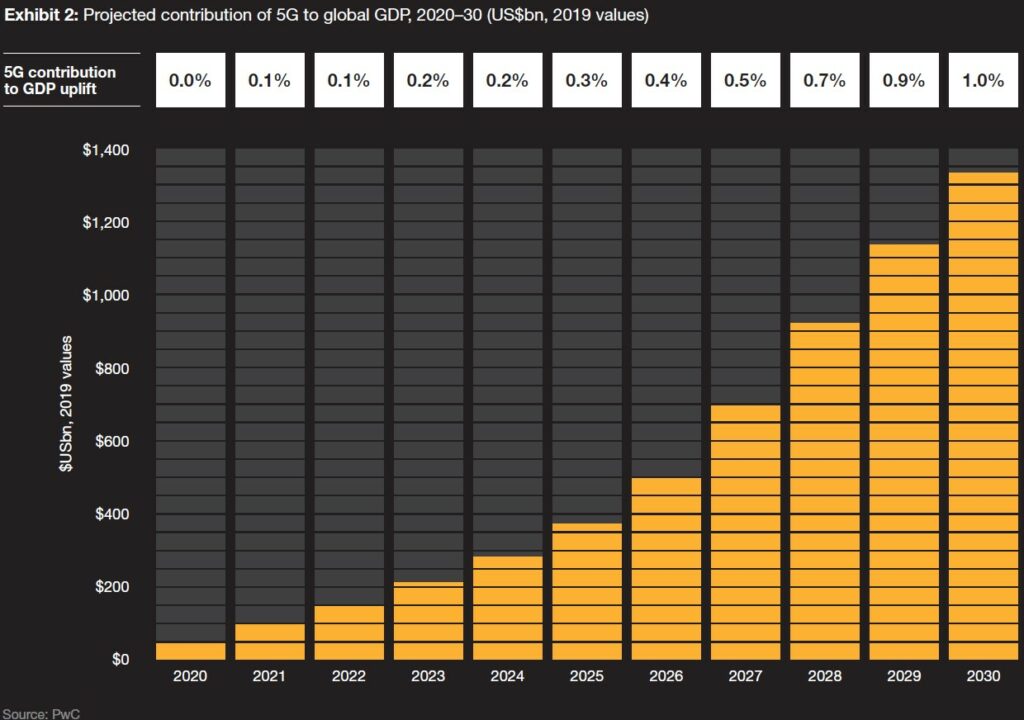
For the next 5 years, 5G’s contribution to economic growth will be fairly modest, as telecom companies focus on infrastructure construction and rollout. But starting in 2025, PWC projects these investments will have an increasingly energizing effect on the global economy, as 5G-enabled applications become more widespread. (PWC report)
At the regional level, North America will experience the biggest percentage uplift to GDP from 5G, followed by Asia and Oceania and then by Europe, the Middle East and Africa (EMEA). In absolute dollar terms, North America also will rank highest, and Asia and Oceania is projected to outpace EMEA because of its larger overall economy. (The scale of a national economy will influence its absolute impact on global GDP: a 2% increase in the US economy is about 6 times the size in dollar terms of a 1.3% expansion in the Japanese economy). (PWC report)
Brazilian communications minister Fabio Faria has said Huawei will not be among the suppliers of the private communications network to be used by the government. He has said Huawei is not apt to participate in the government’s network, to be set up by the winners of the upcoming 5G auction. (Laoyaoba, ZDNet)
U.S. District Judge Rudolph Contreras has put a temporary halt to the ban, siding with Xiaomi in a lawsuit that argued that the move was “arbitrary and capricious” and deprived the company of its due process rights. Contreras has said Xiaomi was likely to win a full reversal of the ban as the litigation unfolds and issued an initial injunction to prevent the company from suffering “irreparable harm”. (Android Central, Bloomberg, My Drivers)
CICC believes that 2020-2025 will be the key 5 years for China to leapfrog toward advanced autonomous driving. According to Roadmap 2.0, China is expected to achieve highly automated driving on highways and valet parking by 2025; highly automated driving on suburban and urban roads is expected to be achieved around 2030; fully automated driving is expected to be achieved after 2035. (CICC report)
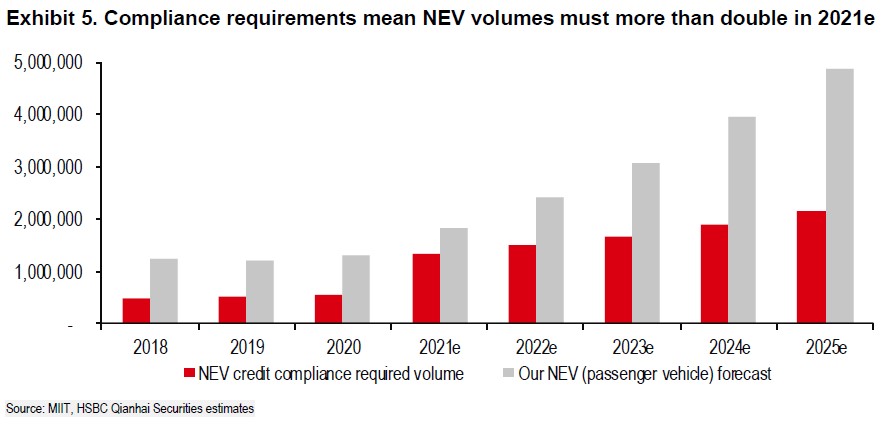
A major driver for China’s conversion to EVs is the dual credit system – where auto makers get credits for compliance features like energy efficiency, or they can buy credits from others, and face penalties if they do not make enough new energy vehicles (NEVs). Under the current NEV regulations, volumes of NEVs for 2021 must more than double from 2020. In 2021, HSBC estimates there needs to be 1.3M sales of NEVs (passenger vehicles) for the overall market to be compliant vs. 0.6M in 2020. This will intensify competition as OEMs will have to meet volume requirements, launch quality products and ensure sufficient scale and profitability. (HSBC report)
In 2020, the top 10 cities made up 48% of new energy vehicles (NEV) volumes in China. The top 6 cities have plate restrictions for ICE vehicles (Beijing is an exception and has plate restrictions on both ICE and NEV plates). HSBC sees part of the NEV demand in those cities as driven by ICE plate restrictions. (HSBC report)
Mini will stop selling gas cars by 2030. The brand also plans to introduce its last gas model in 2025 and for half its sales to be electric by 2027. The plan would make Mini the first brand in BMW Group to go all-electric. (Engadget, Electrek, Der Spiegel, Auto Home)
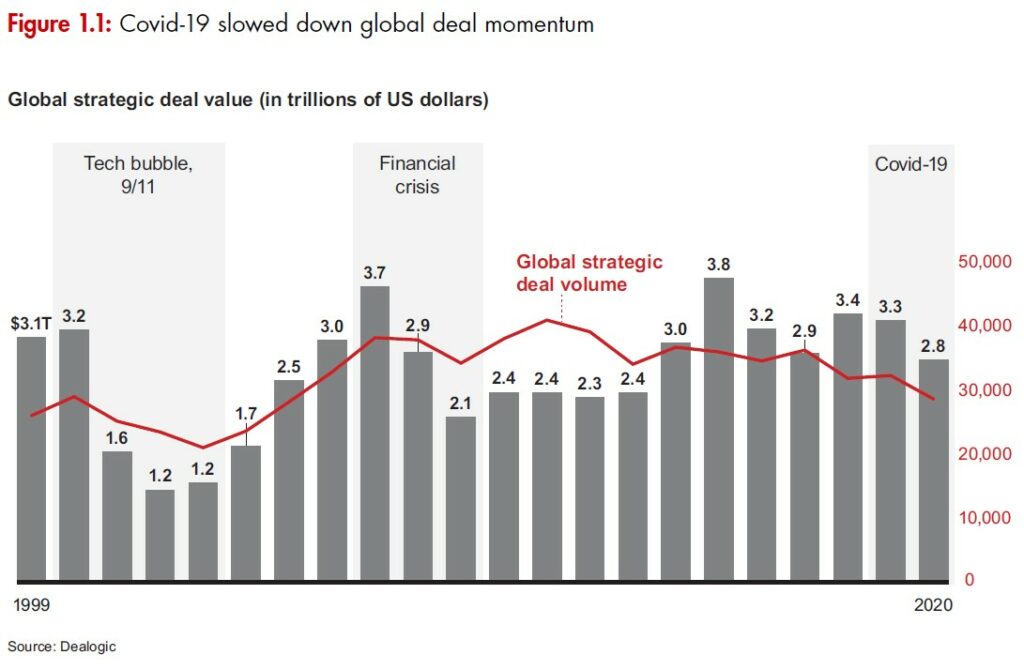
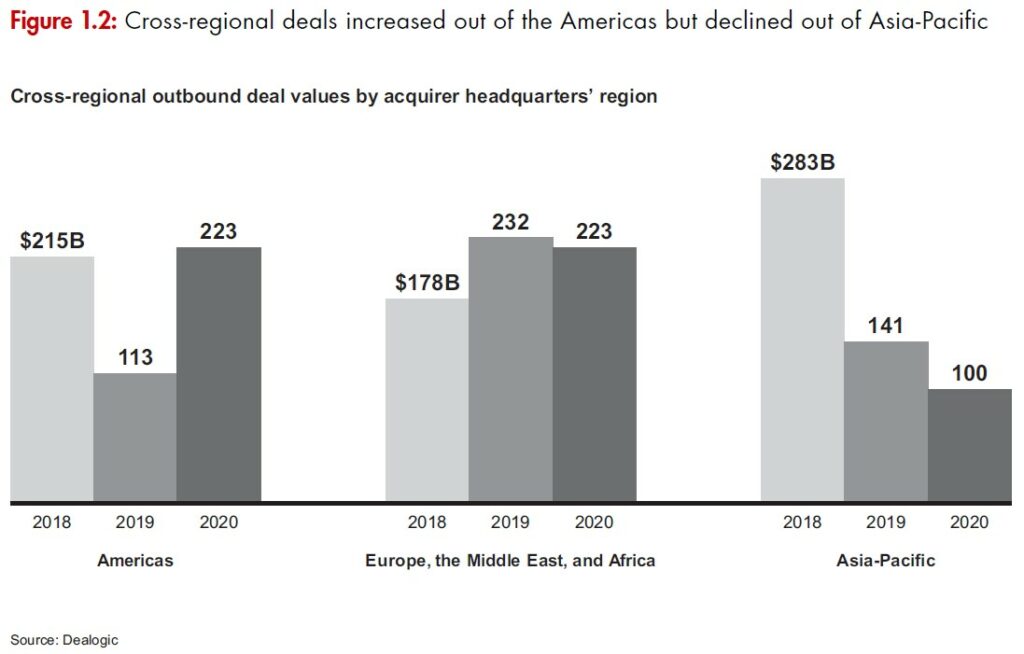
Bain & Company has investigated the impact of the pandemic on the global merge & acquisition deals. In terms of overall deal volume and value, the recovery was not enough to compensate fully for the lean 1H20. Full year 2020 delivered meaningful declines both in value (down 15%) and volume (down 11%) vs. the previous year. By region, the Americas was down 25%, the sharpest regional decline; Asia-Pacific and Europe, the Middle East, and Africa ended the year relatively better, with deal value declines of 4% and 6%, respectively. (Bain & Company report)