
3-21 #Home : CATL is reportedly considering sites across North America; LG plans to drop its automotive wireless smartphone charging unit; GM is acquiring SoftBank Vision Fund 1’s equity ownership stake in Cruise; etc.
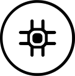
The market is fearing inventory pile-up due to long foundry lead times although on several key factors, chipset shipments look to be tracking not far off the handset shipment actuals: (1) Qualcomm mix over volume. Qualcomm’s entire 4Q21 YoY mobile growth was from ASPs adding the iPhone modem and recovering premium mix, with its unit volume flat YoY, (2) Huawei ban. HiSilicon dropping almost completely from annualized 200M in late 2019, (3) Exynos share loss. Samsung Exynos volumes according to IDC declining from over 60M/quarter in 2H19 to 15M/quarter in 2H21, with Mediatek ramping in, and (4) Mediatek adjustments. Mediatek’s handset unit slowdown in 2H21 kept it flat throughout. (Credit Suisse report)
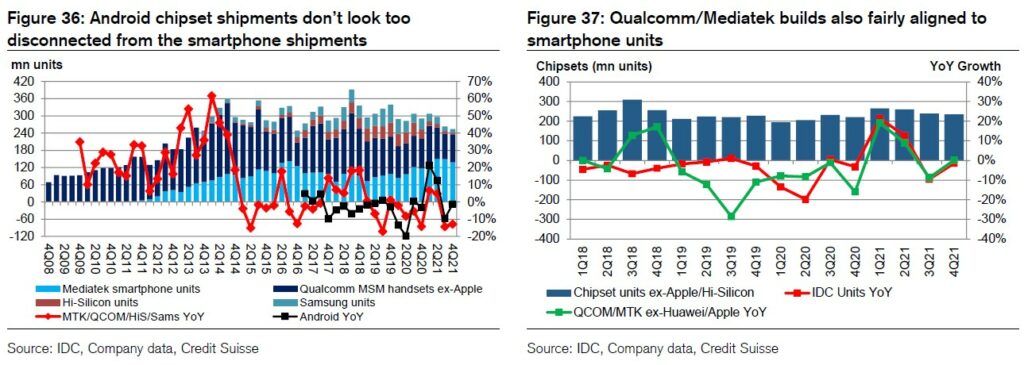
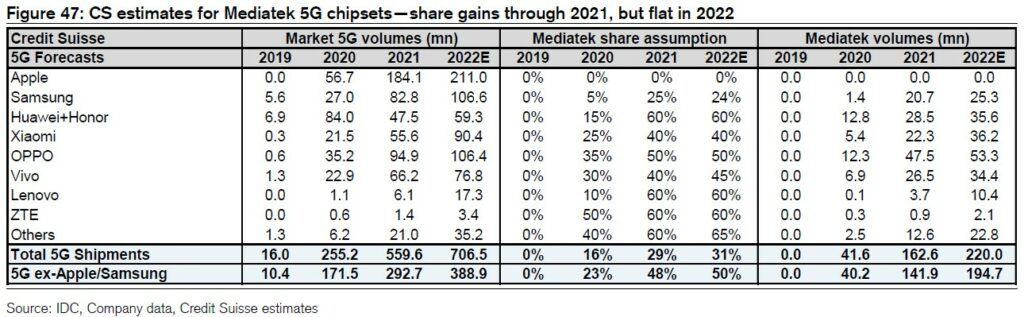
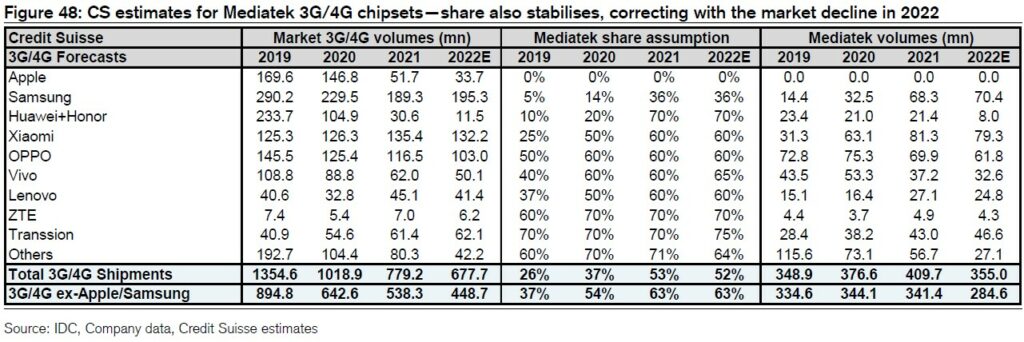
Mediatek has delivered 163M units in 5G shipments in 2021 benefiting from the share gains in Samsung and ex-Apple / Samsung gains post HiSilicon’s ban. With Credit Suisse’s 5G estimates unchanged, they maintain 5G shipment forecast for Mediatek at 220M for 2022. While investors are concerned about Qualcomm supply rebounding from 4Q21, Mediatek can meet their assumption in 2022 with little further gain at 31% of 5G and 50% of 5G ex-Apple / Samsung in 2022.(Credit Suisse report)
There are big differences in the process requirements of different automotive chips. 1) Functional chips mainly rely on mature manufacturing processes. Since automotive chips are not limited by space, the requirement for high integration is not very urgent, and the main functional chips are used in low computing power fields such as generators, chassis, and security. Safety, reliability and low cost are the main considerations, and mature manufacture process meets those needs. Thus, we see that the technology for making most of the chips needed in cars is 15 years old or earlier. To further reduce costs, the chip industry started using 300mm wafers after 2000, but most of the older 200mm production lines continue to be used. 2) The main control chip continues to move towards the high-end process. In recent years, with the development of automotive intelligence, the urgent need for higher computing power for higher-level autonomous driving is driving the extension of the automotive computing power platform process to 7nm and below. (PingAn Securities report)
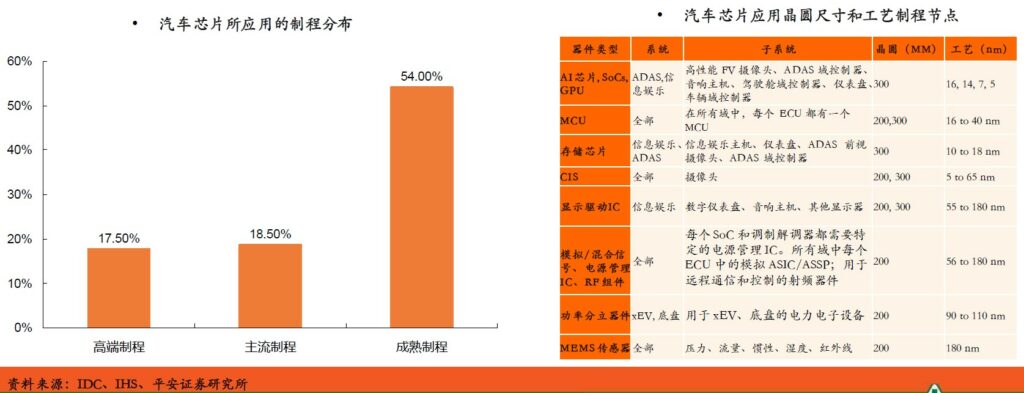
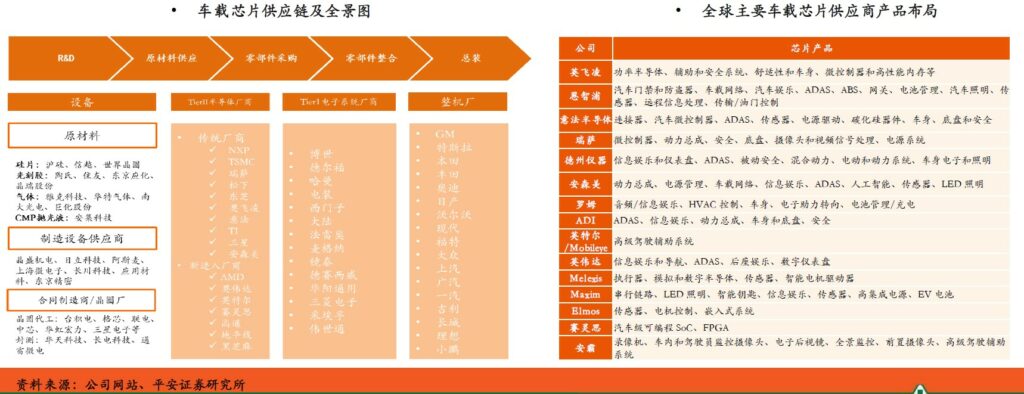
Automotive chip manufacturers generally participate in the entire automotive supply chain as Tier 2 (second-tier suppliers), and the competitive landscape of traditional chip (functional chip) manufacturers is relatively stable. Companies such as Infineon, NXP, Renesas, STMicroelectronics, and Texas Instruments are among the top the forefront of the market, it has its own expertise in MCU, power semiconductors, sensors and other sub-segments, and has formed a solid supply relationship with Tier1 (first-tier suppliers). In recent years, with the increase in computing power requirements for autonomous driving, the demand for large computing power, especially AI chips, has increased. Players in intelligent computing and consumer-level racing tracks have begun to enter this field. Some Chinese startups also have a place in this field. (PingAn Securities report)
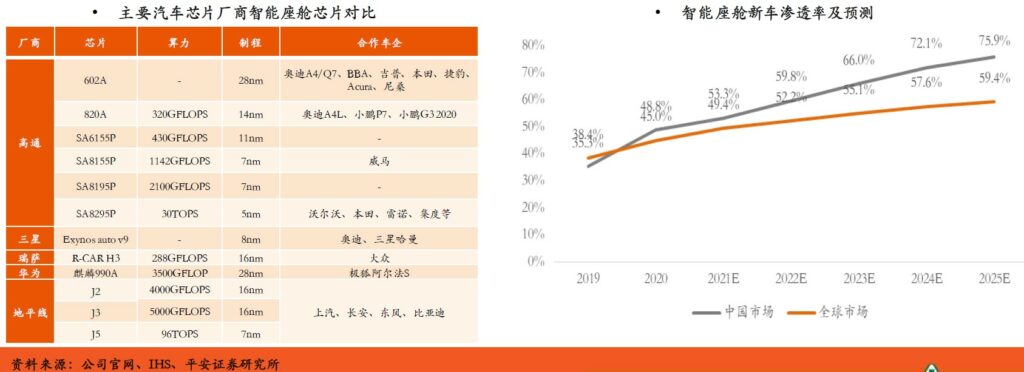
The main players of cockpit chips include traditional automotive chip manufacturers such as NXP, Texas Instruments, and Renesas Electronics, as well as manufacturers in the consumer electronics field such as Qualcomm and Samsung. Globally, Qualcomm has obvious advantages in the mid-to-high-end cockpit chip market. Its latest product SA8295P adopts the global 5nm process, and has already started cooperation with mainstream car manufacturers. Domestically, Huawei and Horizon Robotics are leading. According to IHS, the penetration rate of smart cockpit new cars in the global market and the Chinese market is increasing YoY, and it is expected to increase to 59.4% and 75.9% respectively in 2025. From a trend point of view, the cockpit chip will focus on the development of “one-core multi-display”, that is, a large chip provides support for the LCD instrument panel and infotainment screen at the same time. The chip itself will also develop in the direction of miniaturization, integration and high performance. (PingAn Securities report)
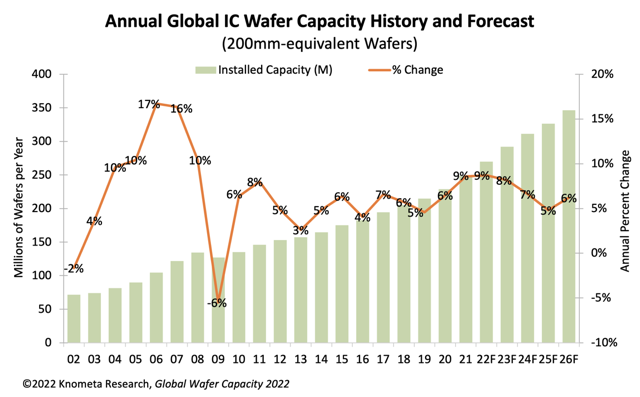
According to Knometa Research, in 2021, IC manufacturers responded to widespread shortages by increasing capacity 8.6%. This was the highest rate since 8.0% in 2011 or 10.4% in 2008. For 2022, an 8.7% expansion of capacity is expected, followed by 8.2% growth in 2023. Capital spending for fabs and equipment, expressed as a percent of semiconductor revenue, was at 25% in 2021, the highest rate since 2001 when the ratio was 26%. In the past, very high spending-to-sales ratios usually indicated too much capacity was being added and a market correction was coming soon. In 2001, capacity utilization rates tumbled sharply from 2000 when chip demand crashed. However, in contrast to 2001, unit shipments in 2021 were very strong, resulting in a high overall utilization rate of nearly 94%. (Laoyaoba, 199IT, Knometa Research)
Cut off from those suppliers by US sanctions, Huawei has turned instead to Arm. As sanctions now target Russia, Huawei’s Moscow data center has suddenly assumed a more critical role. The cloud business this sort of infrastructure underpins now appears to be thriving. Huawei does not break out results and has yet to publish headline figures for 2021, but the enterprise unit that includes cloud grew sales by 23% in 2020, when total revenues increased just 4%. The Western backlash against Russia following its invasion of Ukraine leaves a telecom and cloud vacuum that Huawei may be eager to fill. Unlike Ericsson and Nokia, its 5G kit-making rivals, Huawei has not suspended product deliveries to Russian customers. Yandex, a Russian cloud company, has already been hurt badly by European and US sanctions. On March 3, it warned investors that bankruptcy is a possibility and said its current technology supplies will last for the next 12 to 18 months.(Laoyaoba, Light Reading)
Moov, a data-fueled marketplace for used semiconductor manufacturing equipment, has announced the location of its new headquarters in the 100 Mill building in Tempe, Arizona. Moov is uniquely positioned to solve a problem identified by a U.S. Department of Commerce January report: Less-advanced chips are feeling supply shortages most keenly; they are produced by equipment often no longer in production — an obstacle compounded by the fact that no unified secondary market for equipment exists.(Laoyaoba, Business Wire, BizJournals)

Kryptowire is a provider of cloud-based mobile security and privacy solutions. The company has found serious security and privacy vulnerability. It affects a plethora of mobile devices featuring chips from the Chinese maker Unisoc. the chipset has a flat that, if exploited, allows hackers to get their hands on user data and the functionality of the device. It is affecting smartphones with the UNISOC SC9863A chipset. According to Kryptowire, the issue may allow attackers to gain access to call and system records, text messages, contacts, and other private data. They can also video record the device’s screen or utilize the external-facing camera to capture video, or even remotely operate the device, modifying or erasing the data. (Fonearena, Kryotowire, GizChina)
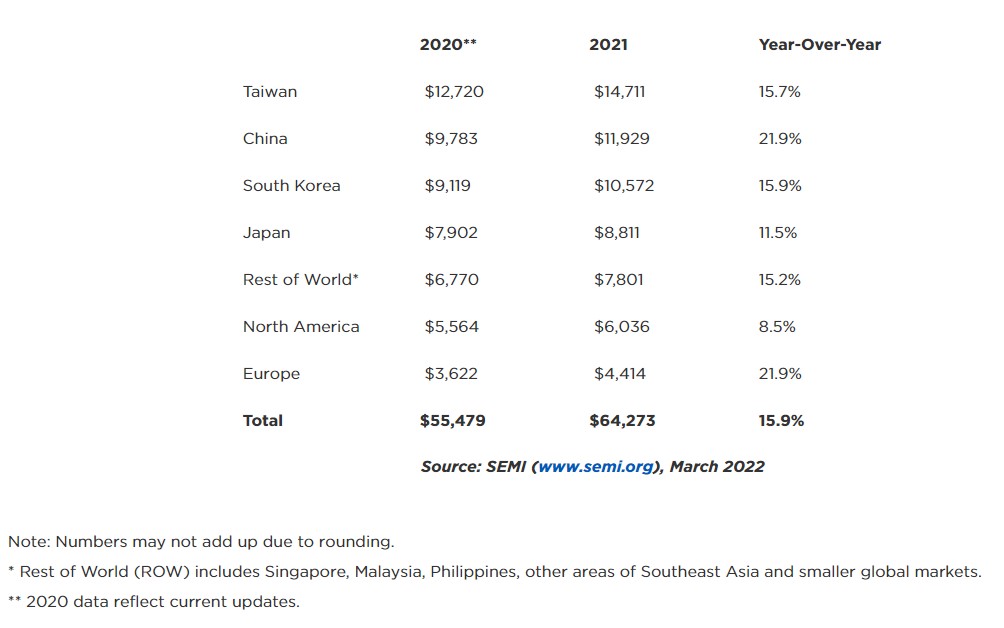
The global semiconductor materials market grew 15.9% to USD64.3B in revenue in 2021, surpassing the previous market high of USD55.5B set in 2020, according to SEMI, the global industry association representing the electronics manufacturing and design supply chain. Wafer fabrication materials and packaging materials revenues in 2021 totaled USD40.4B and USD23.9B, respectively, for year-over-year increases of 15.5% and 16.5%. The silicon, wet chemicals, chemical-mechanical planarization (CMP), and photomask segments showed the strongest growth in the wafer fabrication materials market, while packaging materials market growth was largely driven by the organic substrates, leadframes, and bonding wire segments. (Laoyaoba, Evertiq, SEMI)

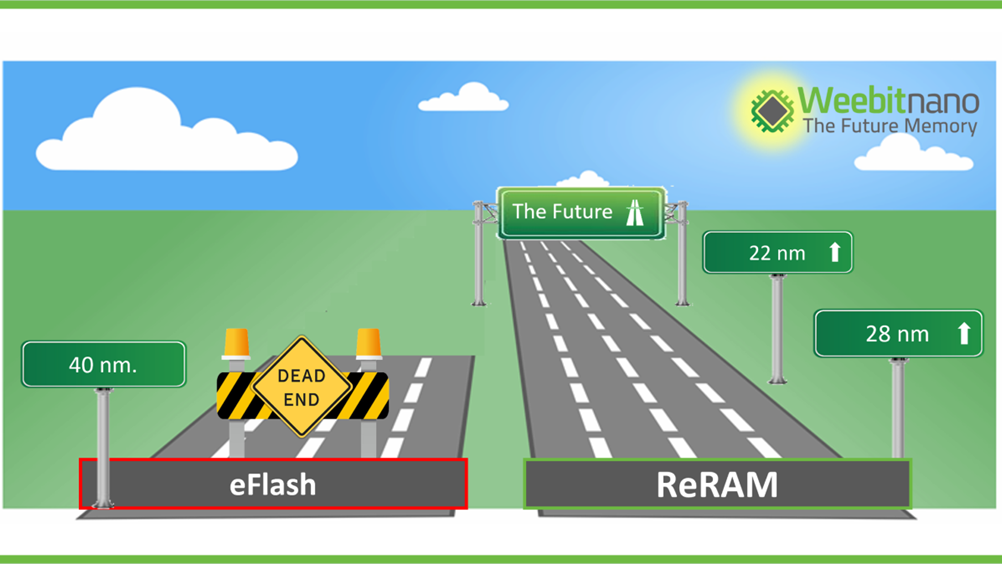
Weebit Nano, a leading developer of next-generation memory technologies for the global semiconductor industry, is pleased to announce that together with CEA-Leti it is scaling its embedded Resistive Random-Access Memory (ReRAM) technology down to 22nm – one of the industry’s most common process nodes. The two companies are designing a full IP memory module that integrates a multi-megabit ReRAM block targeting an advanced 22nm FD-SOI process. Weebit’s first silicon wafers that integrate its embedded ReRAM module at 130nm have shown positive early test results, and the Company has successfully demonstrated production level parameters at 28nm. (Laoyaoba, Globe Newswire, Design Reuse)

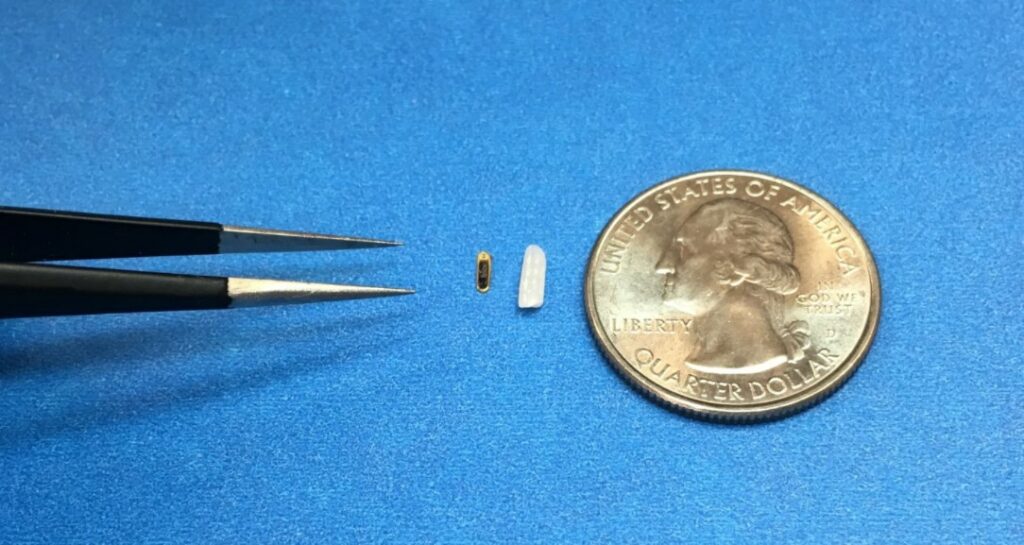
Injectsense, an eye implanter startup, has just got a USD1.7M grant for its implants that are said to be smaller than a grain of rice. It stays immobile for up to 80 years after being implanted to the back of a person’s eye. The new approach aims to make the process of data collection more convenient for doctors to measure the stress level of the owner’s eye (s). One of the most important uses for measuring intraocular pressure is to know the risk of glaucoma, which can actually lead to blindness. Injectsense aims to help steamline the process by giving doctors access to wireless intraocular pressure data through an implant by measuring the amount of built-up tension.(CN Beta, Tech Times, TechCrunch)

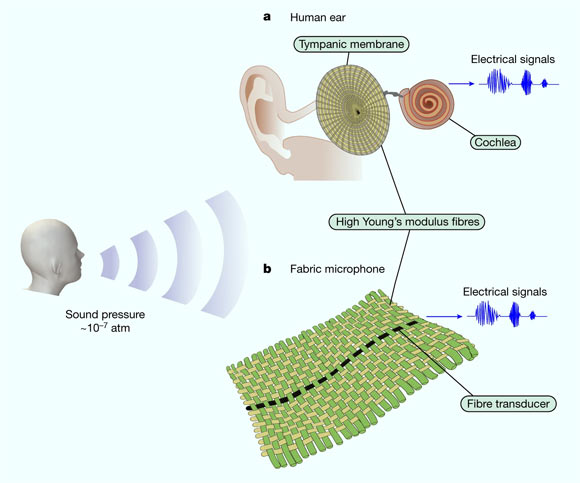
Fabrics have recently been shown to store energy, communicate, heat, cool, display and even store and process digital information. Motivated by the extent of fabric usage, its unparalleled proximity to the human body, and the importance of acoustic signals, MIT set out to investigate whether fabrics could serve as efficient sound collectors to detect and process even faint audible signals. The consequences of such a transformation in fabric use would be far-reaching — enabling fabrics to mediate acoustic communications, pick up acoustic health indicators from the body, and increase situational acoustic awareness. (CN Beta, Nature, MIT, Sci-News)

China’s Contemporary Amperex Technology Co Ltd (CATL) is reportedly considering sites across North America for a massive USD5B plant to supply customers including Tesla. The company aims to build a factory capable of producing as much as 80 gigawatt-hours of batteries a year. Lithium iron phosphate, or LFP, batteries are cheaper and more stable than alternatives, but often provide shorter range because they lack energy density — though that is quickly changing. CATL dominates the market for LFP batteries, and Tesla already uses LFP cells supplied by CATL at its Shanghai factory.(Laoyaoba, Bloomberg, CNEVPost)

LG Electronics reportedly plans to drop its automotive wireless smartphone charging unit as the global home appliance giant exited from the loss-making mobile phone business in 2021. LG has decided to sell the division within the company’s Vehicle Component Solutions unit to South Korea’s BH, a Kosdaq-listed smartphone parts maker, for KRW140T (USD115.2M). BH will buy the division through BH EVS, its affiliate for the automotive electronics business.(CN Beta, KED Global)

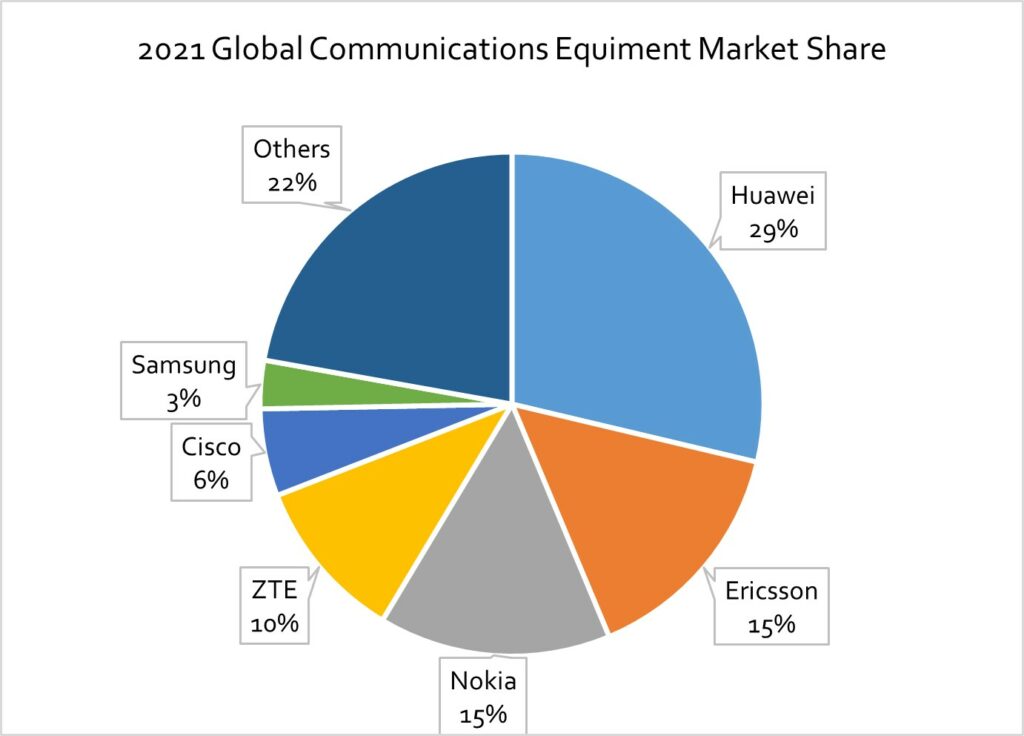
Huawei accounted for 28.7% of the global communications equipment market in terms of sales in 2021, topping the market for two years in a row in spite of declines in sales and smartphone sales volume. Ericsson came in second with 15%, followed by Nokia (14.9%), ZTE (10.5%), Cisco (5.6%) and Samsung Electronics (3.1%). In the global market excluding China, Huawei’s share was 18% and those of Ericsson and Nokia were 20% each. (Laoyaoba, Business Korea)

The smartphone market was slightly light of Credit Suisse’s 22 Nov 2021 forecast for 4Q21, with 4Q21 units up 10% QoQ to 367.6M vs normal seasonal +12% QoQ and shy of their 370M forecast. China shipments were 83.5M, up 3% QoQ from a depressed 3Q21 base and near their forecast of 84.2M. Rest of world was 284.1M, up 12% QoQ but shy of their +13% QoQ forecast and +15% seasonality. Credit Suisse trims their 2022 units to 1.419B / +4.4% YoY (vs previous 1.453B / +6.6% YoY) and 2023 units to 1.486B / +4.7% YoY (vs previous 1.51B /+4.0% YoY) as smartphone sales remain sluggish and held back by inflationary BOM cost pressure and evolutionary feature upgrades. They still expect a modest unit growth both on bottom’s up basis as some vendors recover from production disruptions and improve supply and on top-down view improving mobility helps stabilize replacements to allow some growth. Stable replacement rates and feature phone upgrades in emerging markets would drive modest positive growth continuing from 5-year low levels in 2020 at 1.28B to surpass the 1.47B peak in 2016 by 2023. (Credit Suisse report)
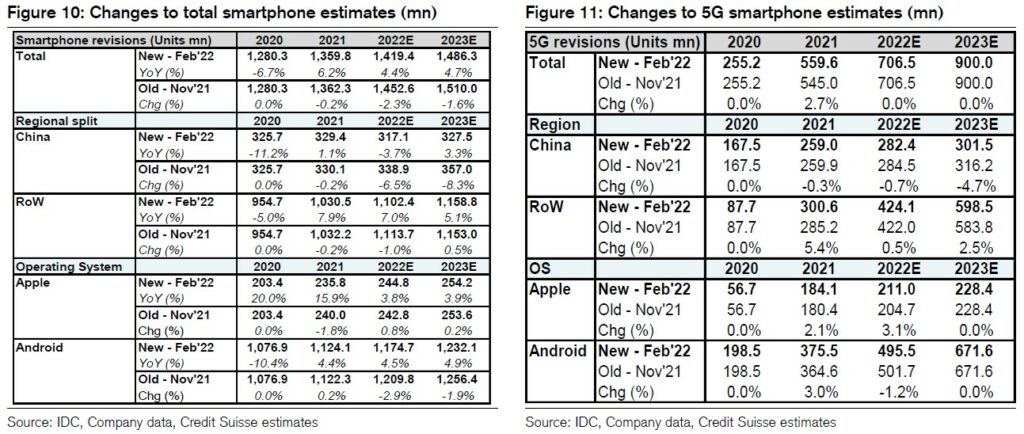
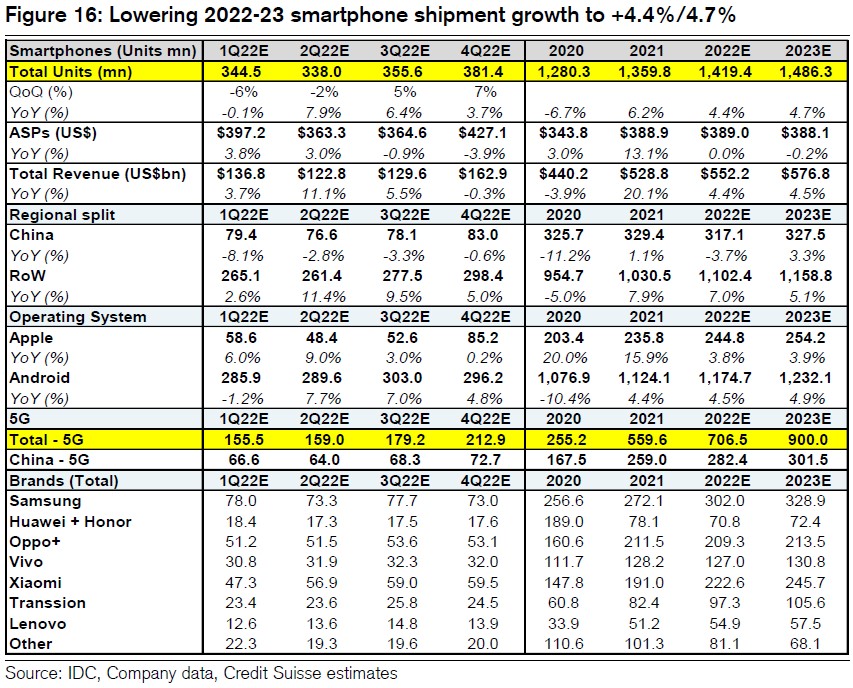
Credit Suisse forecasts shipments mainly driven by growth in RoW vs China which has continued slower replacement rates as 5G pricing has stayed elevated, leading them to cut 2022 from 339M to 317M, -4% YoY. They see re-opening in RoW supporting +7% YoY growth to 1,102M. They only see a slight impact from Russia at 3% of global shipments. The 2022 Android growth of +50M on a bottom’s up basis is driven by analysts expecting unit growth from a few key brands including (1) Samsung recovering from its Vietnam production disruption (+30M to 302M), (2) Xiaomi’s aggressive to ramp up export markets (+32M to 223M), (3) Transsion on rising emerging market smartphone penetration (+15M to 97M) and Lenovo (+8M to 59M) on continued turn-around and strength in the Americas. Otherwise they forecast flattish OPPO and vivo shipments and declines from the Huawei’s portion of Honor and continued consolidation of the smaller brands. (Credit Suisse report)
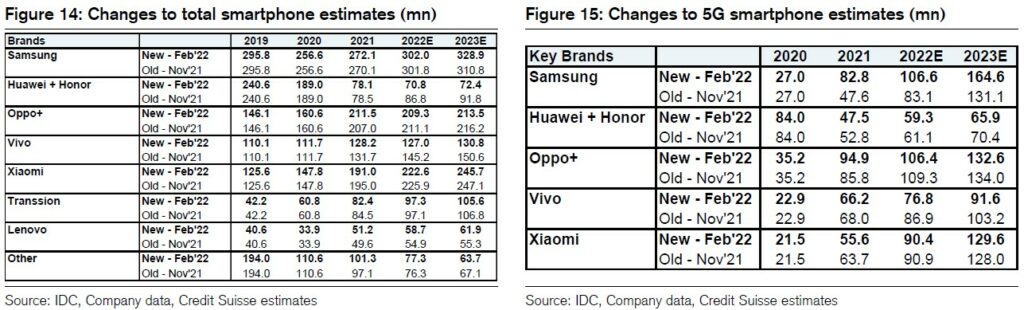
Credit Suisse introduces quarterly estimates for 2022 and view the compares getting easier, as the 2021 profile saw YoY growth decelerate globally from +25% in 1Q21, +13% in 2Q21, -6% in 3Q21 and -2% in 4Q21 on second wave Covid outbreaks, supply chain constraints and weak China consumption. (Credit Suisse report)
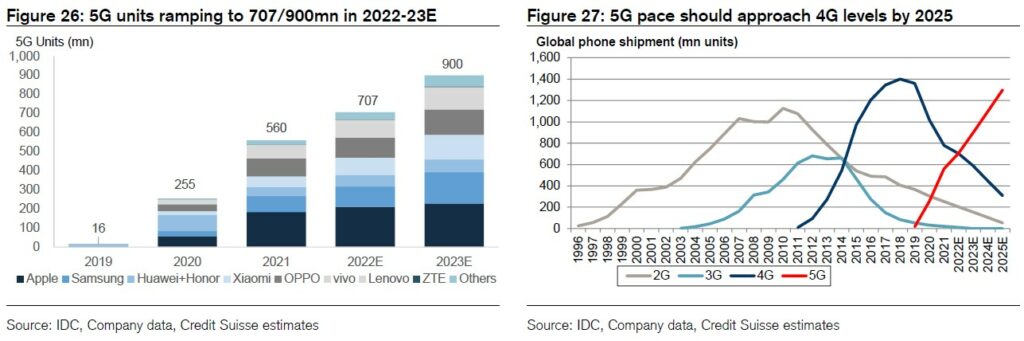
Based on the stronger 2021 5G shipments of 560M units versus Credit Suisse forecast of 545M units, they keep their 5G smartphone units estimates for 2022 / 2023 at 707M / 900M units, despite lowering of their overall smartphone unit estimates on 5G penetration into more markets and lower price points. They expect 5G adoption to expand to 1.3B units by 2025, approaching the 4G levels reached during 2017-2019. (Credit Suisse report)
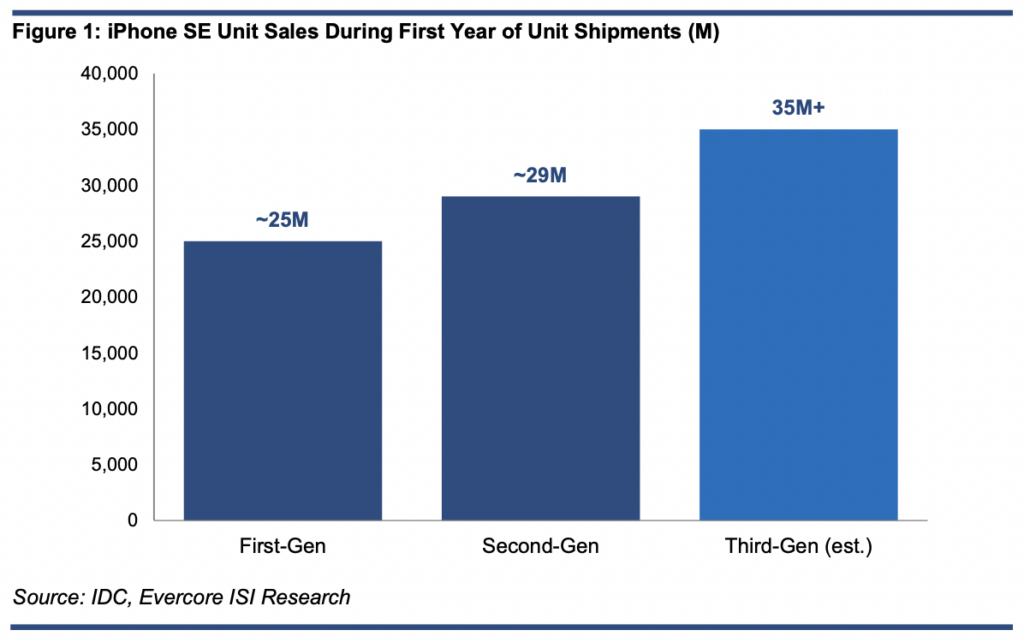
The US investment bank Evercore ISI has estimated that Apple is expected to sell 35M iPhone SE phones in 2022, which will generate an additional USD15B-20B in annual revenue for Apple. Evercore ISI analyst Amit Daryanani is optimistic about the new generation of iPhone SE is mainly based on three reasons. First, the starting price of the new iPhone SE, although 8% higher than the previous generation, is still affordable. (PED30, NASDAQ, CN Beta, Realmi Central)
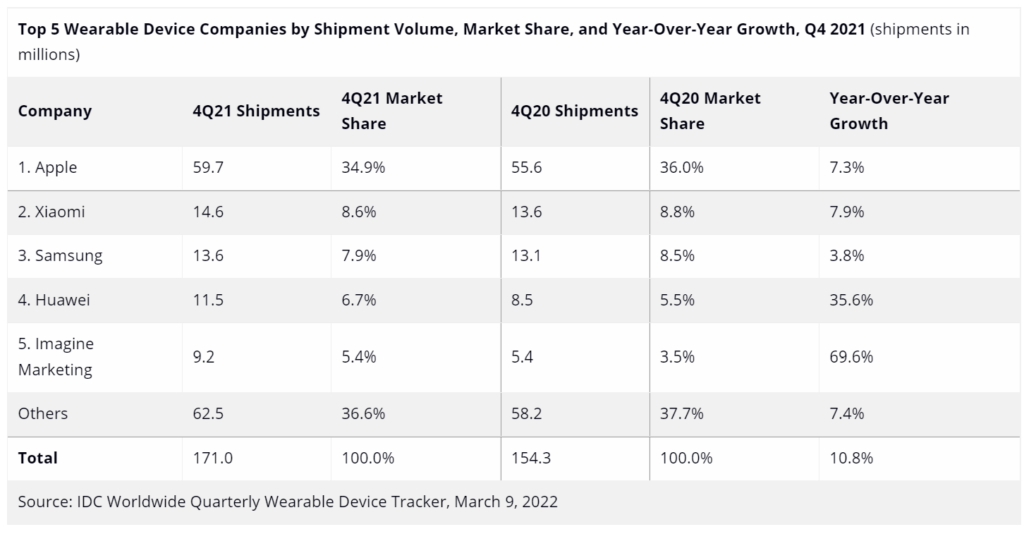
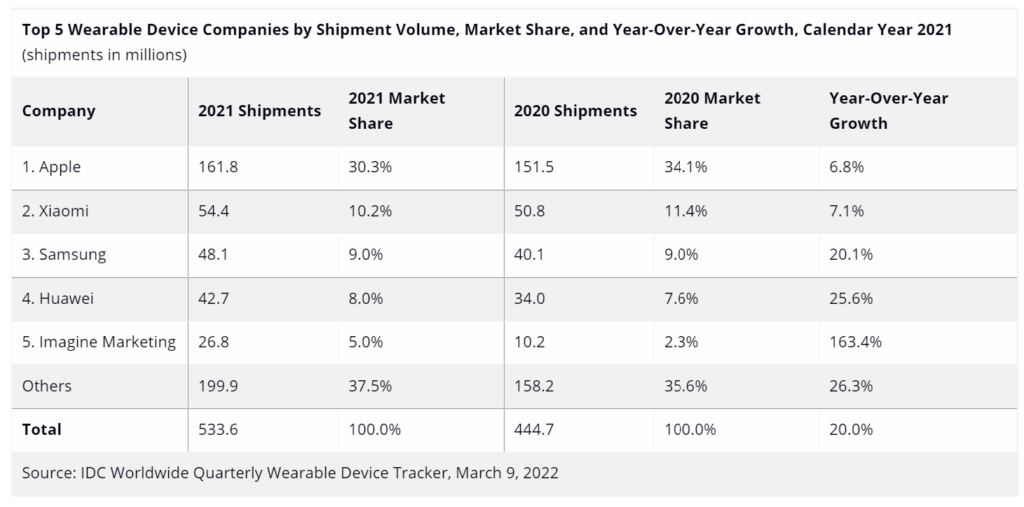
The worldwide wearables market hit a new record high in 4Q21 as shipments reached 171M units, up 10.8% from the same quarter last year, according to IDC. New products and continued demand for health and fitness tracking products along with hearables helped the market maintain its momentum. Shipments for the full year 2021 totaled 533.6M units, an increase of 20.0% over 2020. Hearables were once again the leading category as shipment volume grew 9.6% during the quarter and accounted for almost two-thirds of the entire wearables market. Meanwhile, watches continued to steal share from wristbands as the larger form factor offers consumers more features and customization. (IDC, CN Beta)

General Motors (GM) has announced it is acquiring SoftBank Vision Fund 1’s equity ownership stake in Cruise for USD2.1B and separately will make an additional USD1.35B investment in Cruise, replacing a previous commitment made by the fund in 2018. Since GM acquired a majority ownership stake in 2016, Cruise has made self-driving cars a reality and is a leader on the pathway to commercial autonomous ridesharing and delivery, creating significant value for both GM shareholders and Cruise’s minority shareholders.(Engadget, General Motors)
AVATR 11, the first model of the joint venture between Huawei, Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL), and Changan Automobile, is revealed. In terms of intelligent driving, the new vehicle is equipped with Huawei’s ADS system, and can implement L2-level automatic assisted driving. It has more than 30 sensors with a computing power as high as 400 tops. Further, the console features Huawei’s HarmonyOS intelligent system. AVATR’s design center is located in Germany and this model was also designed by a German team. The vehicle is equipped with CATL’s ternary lithium-ion battery pack and its new generation cell-to-pack technology (CTP). CTP adopts the scheme of integrating small modules into larger modules which means that there are still modules, but the number of modules is fewer but the energy density of the batteries is much higher.(CN Beta, My Drivers, QQ, Sohu, Pandaily, AutoTech)

Ford will soon start selling and shipping some Ford Explorers without the chips that power rear air conditioning and heating controls. Ford spokesperson Said Deep has indicated that heating and air condition will still be controllable from the front seats, and that customers who choose to purchase a vehicle without the rear controls will receive a price reduction. According to Deep, Ford is doing this to bring new Explorers to customers faster, and that the change is only temporary.(The Verge, Auto News)