12-27 #CoughCough : TSMC lowered its capital expenditure in 2022 to USD36B; Samsung to ramp up its wafer production capacities for memories and system semiconductors by around 10% in 2023; Huawei and Nokia have announced the extension of their patent license agreement; etc.
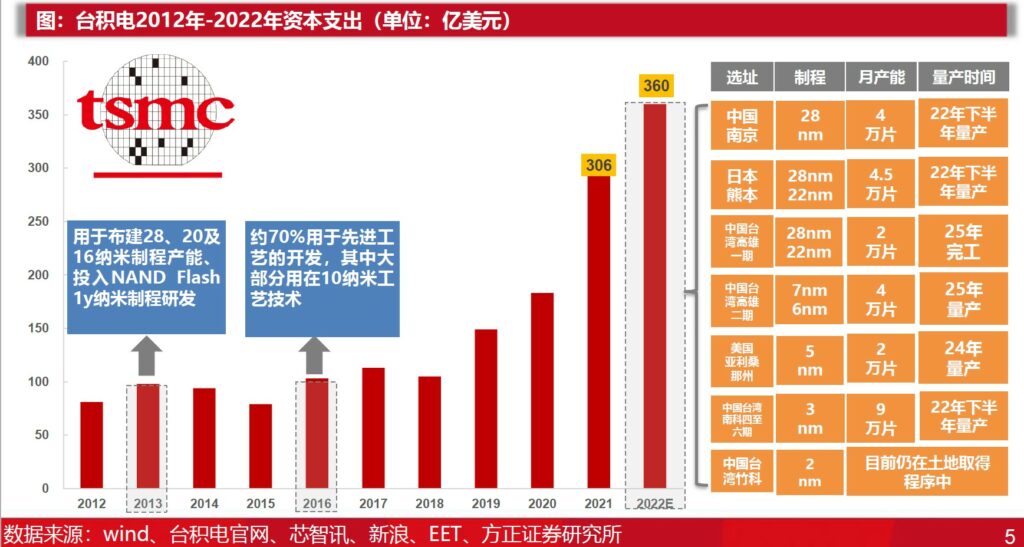
Affected by weak consumer demand and the upstream supply chain, TSMC lowered its capital expenditure in 2022 to USD36B, which was previously expected to be USD40-44B. In terms of demand, the company also expects that the industry’s inventory level will reach its peak in 3Q22 and begin to decline slowly in 4Q22. The complete destocking adjustment cycle is expected to last until 1H23. (Founder Securities report)
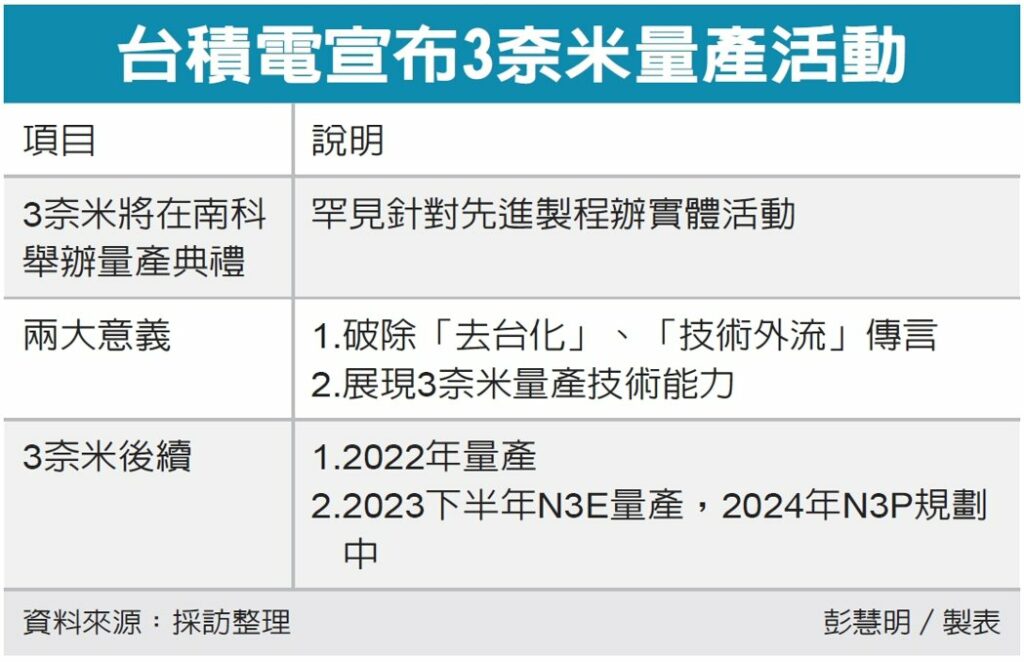
TSMC is scheduled to hold a ceremony at Fab 18 at the Southern Taiwan Science Park (STSP) on 29 Dec 2022 to mark the start of commercial production of chips using 3nm process technology. The pure-play foundry will also detail plans to expand 3nm chip production at the fab. Apple currently uses TSMC’s 4nm process in the A16 Bionic chip in the iPhone 14 Pro series but could jump to 3nm as soon as early 2023. The upcoming M2 Pro chips would be the first to be based on the 3nm process. The M2 Pro chip is expected to debut first in updated 14” and 16” MacBook Pros early 2023 and possibly updated Mac Studio and Mac mini models.(Apple Insider, GizChina, MacRumors, Digitimes, Yahoo, UDN)
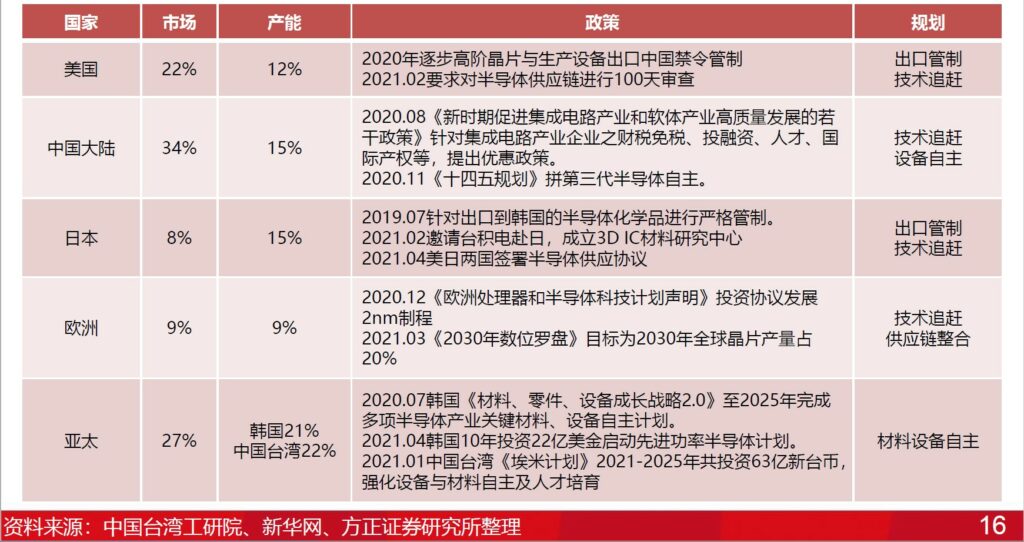
Governments of various countries are actively offering incentives to manufacturers with chip manufacturing capabilities and encouraging manufacturers to set up factories locally. For example, in 2020, TSMC, with the support of the United States, decided to invest USD12B in the United States to produce the world’s most advanced 5-nanometer chips. TSMC and Samsung Electronics plan to build new wafer foundries in the United States, competing for more than USD30B in government subsidies in the United States. China has issued a number of policies to strengthen the country through science and technology, and established a national integrated circuit industry investment fund. The mainland supports the development of local industries. (Founder Securities report)
According to CCS Insights, by 2025, Apple’s annual spending on custom silicon exceeds USD10B. Apple’s decades-long journey to design and build its own chips continues to expand with M series processors for Macs and iPads. The expected addition of a custom 5G modem into iPhones is estimated to account for an additional USD2B in total spending on custom silicon. Although Apple is not considered a semiconductor manufacturer, its expenditure places it in the top 12 globally in terms of semiconductor revenue. Apple cracks the global top 10 rankings by 2026 as it relies more on in-house silicon for its growing product lines. (CCS Insights report)
Texas Instruments (TI) has recently kicked off production for analog and embedded products at its LFAB fab in the US state of Utah, the 12” wafer fab TI acquired from memory chipmaker Micron Technology about one year ago, according to the IDM. TI announced that LFAB will enter mass production of analog and embedded products one year after the purchase , which is TI’s second 12” fab to start mass production in 2022. Texas Instruments said that LFAB provides manufacturing capacity that meets the needs of customers for decades to come, and RFAB2, located in Richardson, Texas, has entered initial mass production in Sept 2022. (Laoyaoba, Digitimes)

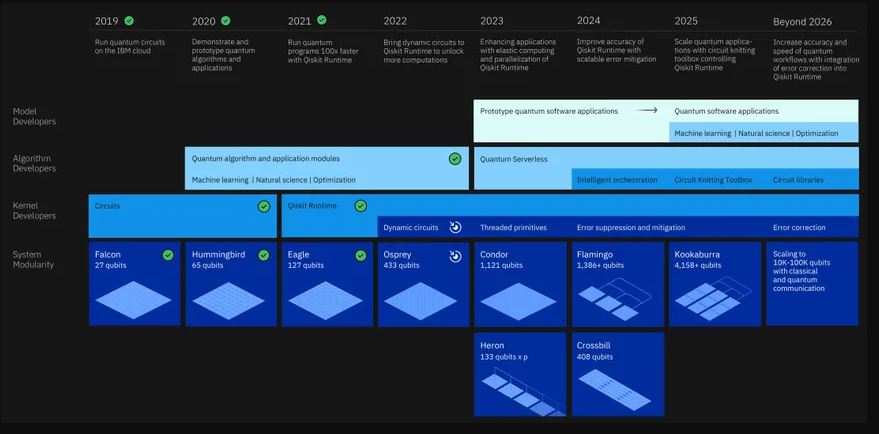
An update to IBM’s quantum-computing road map now says the company is on course to build a 4,000-qubit machine by 2025. But getting the device to do anything useful will require the development of a powerful new software stack that will help manage errors, share the load with classical hardware, and simplify the programming process. Since IBM first unveiled its quantum hardware plans in 2020, the company has largely kept to the schedule; the most recent milestone from that forecast that has come to fruition was the release of the company’s 127-qubit Eagle processor in Nov 2021. The first iteration of the road map topped out with the 1,121 Condor processor that is scheduled for release in 2023, but now the company has revealed plans for a 1,386-qubit processor, called Flamingo, to appear in 2024 and for a 4,158-qubit device called Kookaburra to make its debut in 2025.(Laoyaoba, IEEE, Fierce Electronics)

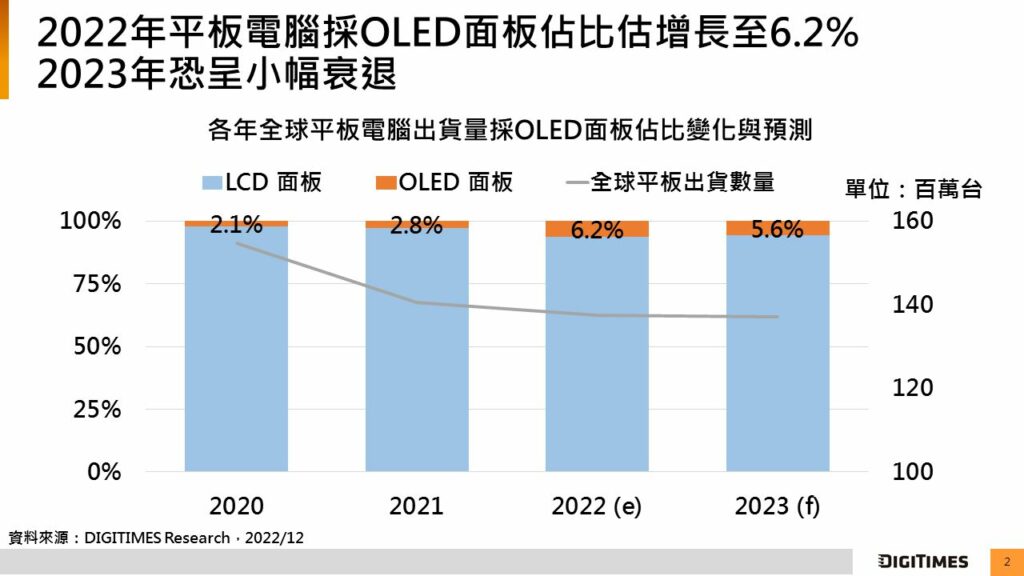
Of the global tablet shipments in 2022, models equipped with OLED panels will account for 6.2%, up 3.4pp from a year ago, while Samsung Electronics, Huawei and Lenovo will be the number-1 to number-3 OLED tablet brands worldwide, respectively, in the year, according to DIGITIMES Research. (Digitimes, Digitimes)

Google’s upcoming Pixel 8 smartphone lineup will reportedly feature an upgraded Samsung camera sensor, ISOCELL GN2, which features the staggered high dynamic range (HDR) functionality for better dynamic range in photos and videos. The existing Pixel phones use the ISOCELL GN1 camera sensor, which lacks Staggered HDR. Google Pixel 8 series is reportedly to be launched in 2H23. (Digitimes, SamMobile, Business Standard)

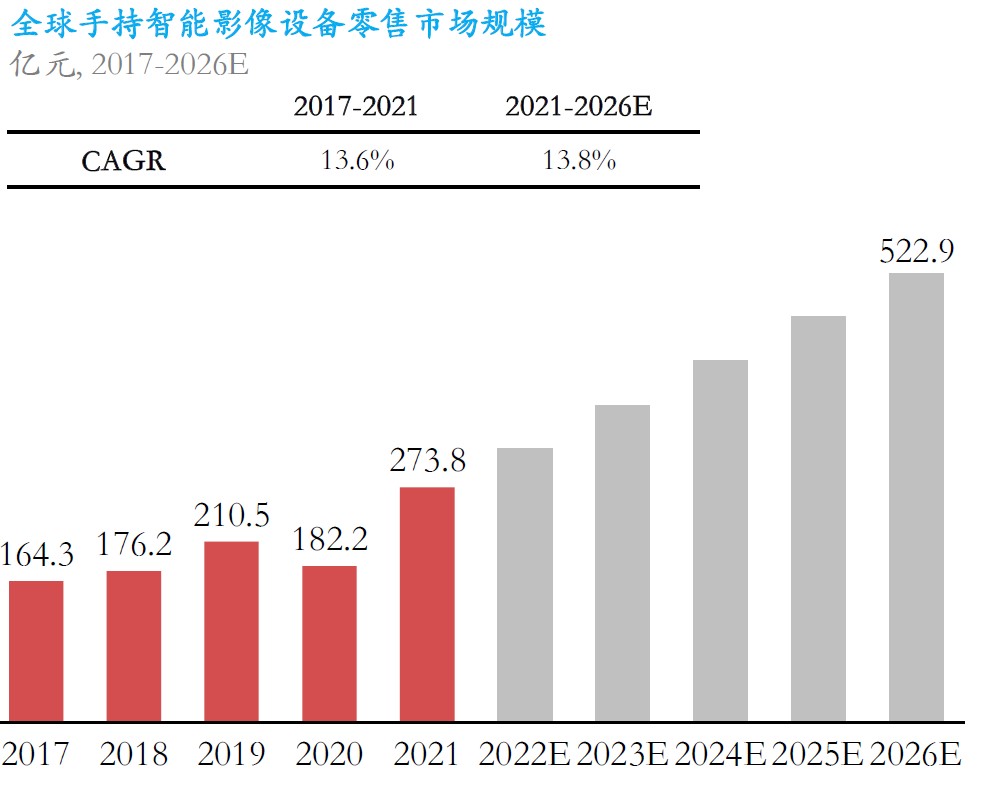
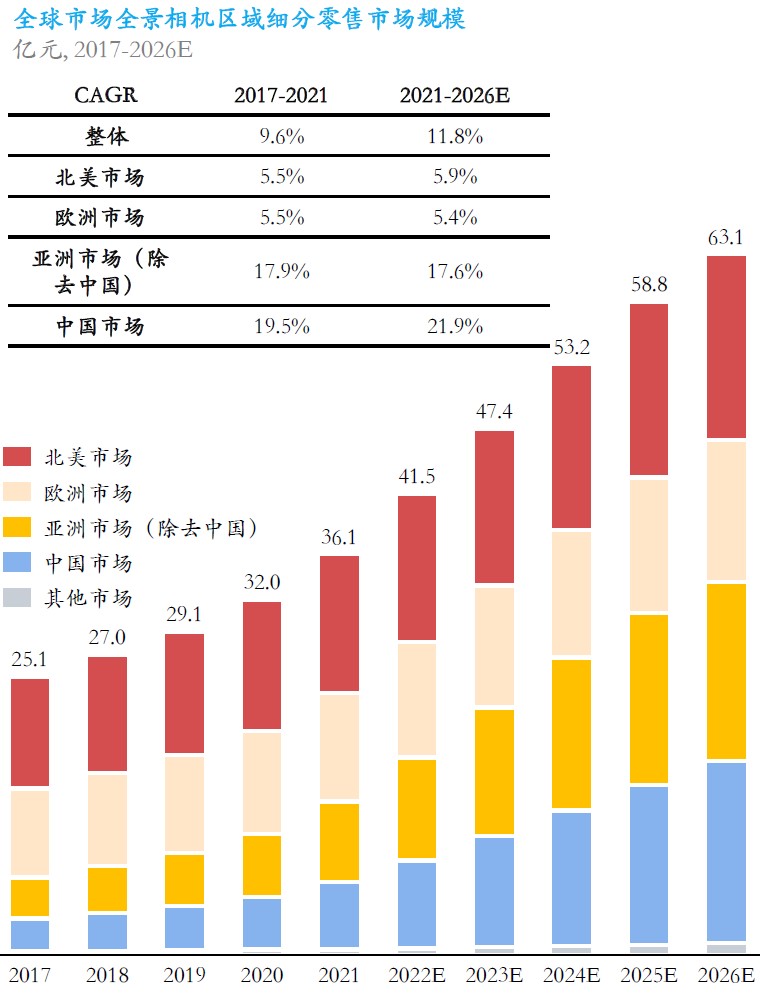
Driven by the brands such as GoPro and Insta360, the consumer-grade handheld smart imaging device market has continued to grow in size in recent years. By 2021, the global handheld smart imaging equipment market will grow from CNY16.43B in 2017 to CNY27.38B in 2021, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.6%. Today, consumer-grade handheld smart imaging devices have initially rolled out in the market, and the industry is expected to enter a period of rapid growth. For the global regional market segments, panoramic cameras accounted for the largest sales share in the North American market. Secondly, the European market ranks second in the overall panoramic camera market. Compared with other markets, the Chinese market is still relatively small, accounting for about 17% of the market, but maintains a relatively optimistic growth rate. (Frost & Sullivan report)
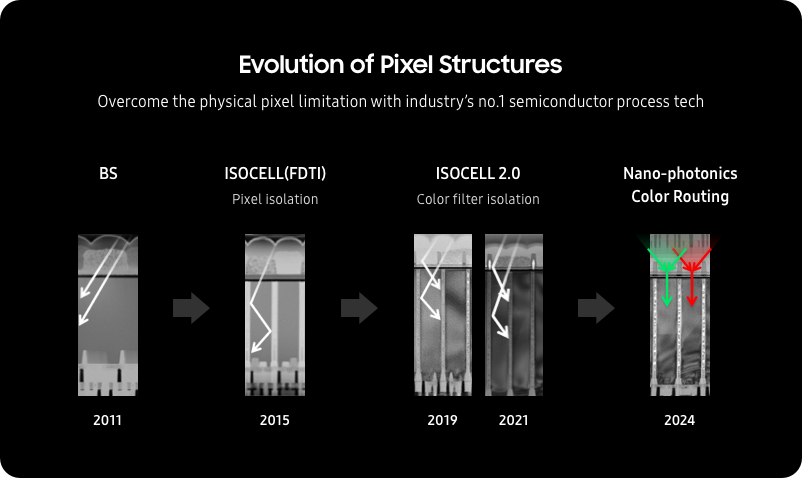
Samsung has introduced ISOCELL, its first technology that isolates pixels from each other by adding barriers. The name ISOCELL is a compound word from the words “isolate” and “cell”. By isolating each pixel, ISOCELL can increase a pixel’s full well capacity to hold more light and reduce crosstalk from one pixel to another. Since its inception, the ISOCELL pixel technology has continuously evolved and its new generation of advancements are being applied to the latest image sensors. For instance, ISOCELL now adds optical walls made up of innovative low refractive material between the color filters. In addition to that, they are developing another innovative high refractive nano-structure to utilize the light of adjacent pixels to extreme levels. By applying these nano-photonics technology, achieving high sensitivity that goes beyond the usual limits.(Samsung, Laoyaoba)

Samsung Electronics has decided to ramp up its wafer production capacities for memories and system semiconductors by around 10% in 2023. Samsung Electronics will establish new DRAM and semiconductor foundry lines with a capacity of producing 100,000 12” sheets of wafer per month at its third plant (P3) in Pyeongtaek, Gyeonggi Province, by 2H23. As for DRAMs, a new facility capable of producing 70,000 sheets of wafer will be added to Samsung’s current lines, which can produce about 20,000 12” wafer sheets per month. For reference, Samsung Electronics produced a total of 665,000 sheets of wafer per month for DRAM production in 3Q22. This new facility is expected to mass-produce advanced 12nm DRAMs recently announced by Samsung. Samsun’s plan to expand facility investment in 2023 is not limited to scaling up wafer production. It also decided to install more than 10 units of extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography equipment for high-tech DRAM and foundry production. It currently has about 40 units of EUV equipment.(Laoyaoba, Business Korea)
Despite Micron and SK applying large-scale cost-cutting measures in a way to tackle notable sequential declines in revenue and margins, it is very unlikely Samsung Electronics, the leader in memory chips, will change its stance on the chip production issue. The baseline is that Samsung is still positioned to preserve margins until 1Q23, and consumer confidence could recover in 2Q23 at the earliest, with economists expecting inflation to moderate after the Jan-Mar 2023 period. Samsung Electronics is in the process of reducing chip stockpiles. Any decisions by the company to cut its chip output artificially would be a plus factor in terms of short-term supply rebalance. (Laoyaoba, Korea Times)

According to CCS Insights, by the end of 2026, more than 25M people access the Internet through a mobile phone connected directly to satellites. This move beyond traditional cellular network connectivity is driven by technology developed by AST SpaceMobile, rather than satellite capability in the latest smartphones. Partnerships between the US company and telecom operators enable people in remote places to get connected for the first time. Although it bypasses today’s mobile infrastructure, it is seen as a largely complementary service to existing networks. (CCS Insights report)
Huawei and Nokia have announced the extension of their patent license agreement. The terms of the agreement remain confidential between the parties. The announcement indicates appetite for access to Huawei’s next-generation telecom patents remains strong, despite US accusations the Chinese giant poses a threat to national security. (Digitimes, Huawei, Bloomberg, Nokia, Huawei Central)

Accordnig to Credit Suisse, for 2022, smartphone production plans have been lowered from 1.23B units (−11% YoY) as of their previous survey to 1.197B units (−13% YoY) as of the most recent survey. The outlook for production volume in 2023 calls for 1.192B units, for flat or a minor YoY decline. Compared with the previous survey, the lower outlook for volume in 2022 reflects weaker-thanexpected demand for Apple iPhone 14 Plus and production constraints for the iPhone 14 Pro / Pro Max, where demand is brisk. For 2023, the outlook of five major Chinese smartphone makers (Huawei, Honor, OPPO, vivo, Xiaomi) call for production to be flat or down slightly YoY. In addition, the outlook for 5G smartphone production is at 581M units (+3% YoY) in 2022 and 585M units (flat YoY) in 2023. (Credit Suisse report)
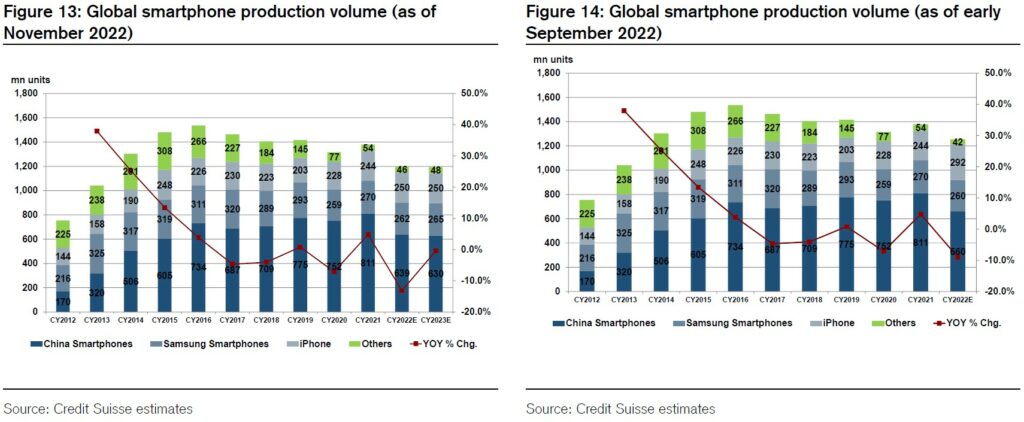
According to Credit Suisse, Chinese smartphone makers produced 811M units (+8% YoY) in 2021. In contrast, the target for 2022 was 884M (+9% YoY) as of Mar 2022. However, as of Jun 2022, plans had been cut by roughly 170M units to 713M, and were lowered again to 660M as of Sept 2022. The figure has now been cut to 630M as of this survey (Nov 2022). Among the five major manufacturers (Huawei, Honor, OPPO, vivo, Xiaomi), all slightly came up short of 2022 production plans apart from OPPO. Credit Suisse expects production volume at the 5 major manufacturers to decline by around 20–40% YoY in 2022, except for Honor. (Credit Suisse report)
There are signs that Samsung may cut off its own voice assistant service, Bixby. Samsung’s voice assistant service started with S Voice on the Galaxy S3. The company then introduced the Bixby voice assistant in the Galaxy S8 launched in 2017. In the past, Samsung has a special Bixby voice wake-up button on the mobile phone hardware. In the OneUI 5.0 update based on Android 13, Samsung introduced a Good Lock module called RegiStar. Through this module, you can personalize the power button. Users can choose to open an app or assign it to system functions including Google Assistant. However, the new module does not support its own Bixby voice assistant. (GizChina, IT Home, Android Police)
Apple Japan is being charged JPY13B (USD98M) in additional taxes by Tokyo authorities, apparently for bulk sales of iPhones and other devices to foreign tourists that were incorrectly exempted from the consumption tax. Bulk purchases of iPhones by foreign shoppers were discovered at some Apple stores. At least one transaction involved an individual buying hundreds of handsets at once, suggesting that the store missed taxing a possible reseller. Japan offers tax-free shopping for visitors staying less than six months to buy certain goods without paying the country’s 10% consumption tax. However, the exemption does not apply to purchases for resell purposes. (Apple Insider, Asia Nikkei)
Samsung has reportedly begun to introduce support for 5G in entry-level models. The goal is to make all models support a 5G network. However, compared to 4G LTE models, Samsung has “streamlined” some of the 5G models.(GizChina, IT Home)
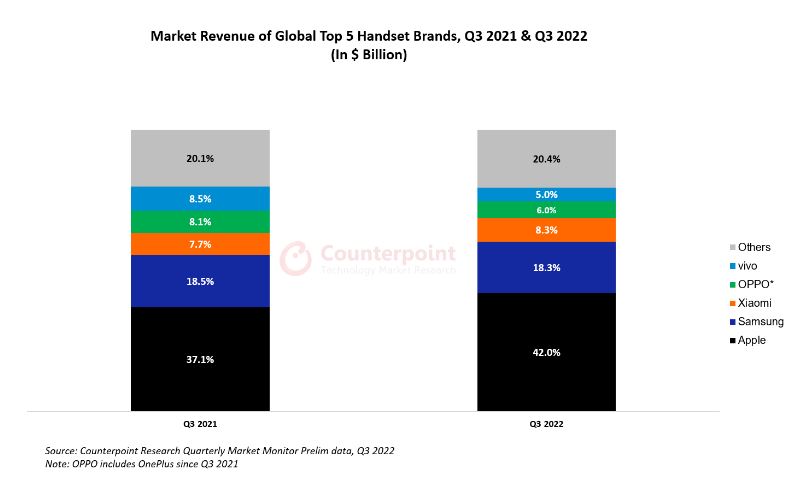
The global smartphone handset market’s revenue declined 3% YoY in 3Q22 to just above USD100B, according to Counterpoint Research. A 10% YoY growth was seen in the average selling price (ASP) thanks to the premium handset segment’s greater resilience to economic uncertainty. The record shipment contribution (46%) of 5G handsets, which cost 5 times an average non-5G handset, also added to the ASP and revenue growth. In terms of shipments, the overall handset market saw a 12% YoY decline during the quarter. Apple saw a 10% YoY revenue growth and 7% YoY ASP growth in 3Q22, contributing to an overall increase in global handset ASP. (Gizmo China, Counterpoint Research)
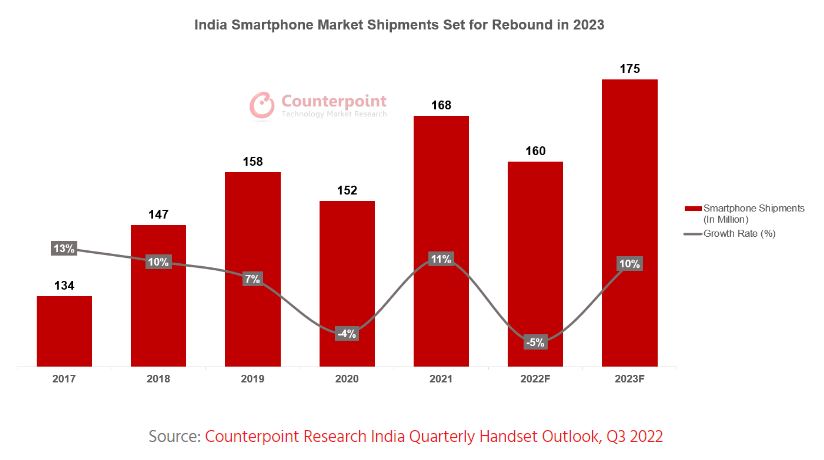
According to Counterpoint Research, India’s smartphone shipments are expected to fall 5% YoY in 2022, dipping for the second time in the last 3 years. Weak demand in entry-level segments hit sales even as the premium segment continued to grow. The market is expected to grow by 10% in 2023 to reach 175M units. The premium market continued to grow in 2022 with the >INR30,000 (USD400) price band reaching a new high. The continued premiumization of the market is the main reason why it saw positive revenue growth with the highest-ever average selling price (ASP) of close to INR20,000 (USD250). (Counterpoint Research, Laoyaoba)

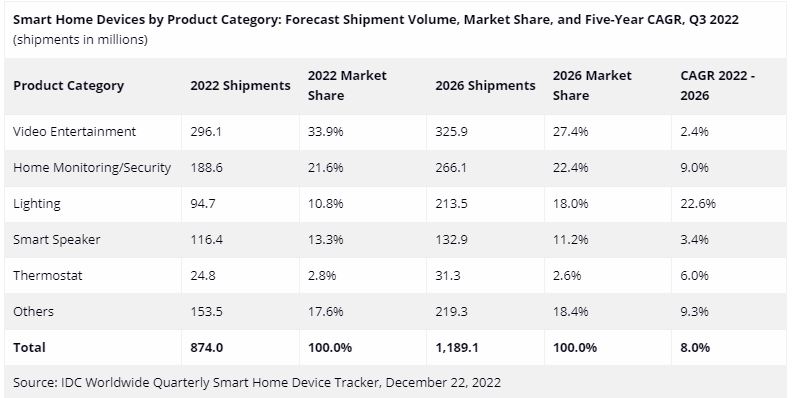
Worsening macroeconomic conditions have led a reduction in the outlook for global smart home device shipments according to IDC. Worldwide shipments of smart home devices are now expected to decline 2.6% in 2022 to 874M units with smart speakers and video entertainment devices such as TV and streaming devices facing the brunt of the decline. Though the global market is forecast to return to growth in 2023, it will remain relatively low at 4.6% with most of the growth coming from emerging markets as well as China. (Digitimes, IDC)

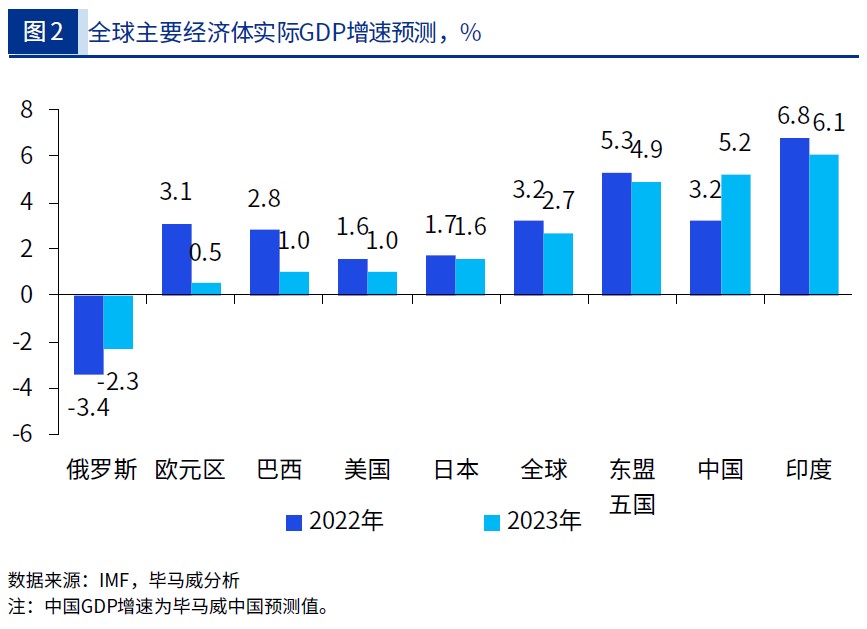
In the latest “World Economic Outlook” report in Oct 2022, the IMF lowered the global economic growth rate in 2023 to 2.7%, and pointed out that the economies accounting for about one-third of the world’s total economic output will be at least The economy contracted for two consecutive quarters. At present, China’s total economic volume has exceeded CNY114T. It is the second largest economy in the world, accounting for more than 18% of the global economy. It is not easy to achieve a growth rate of 5.2% on such a large volume. (KPMG report)